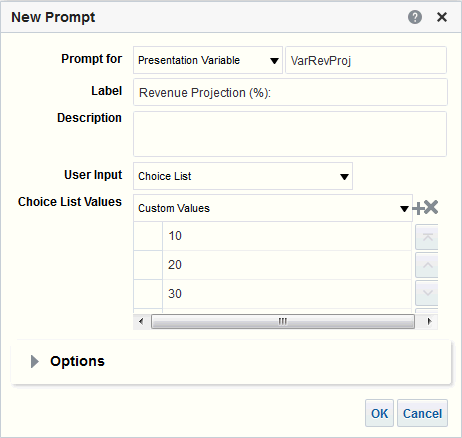
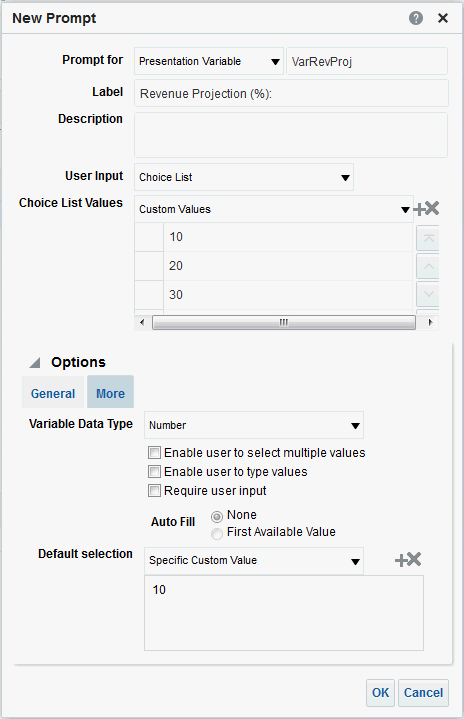
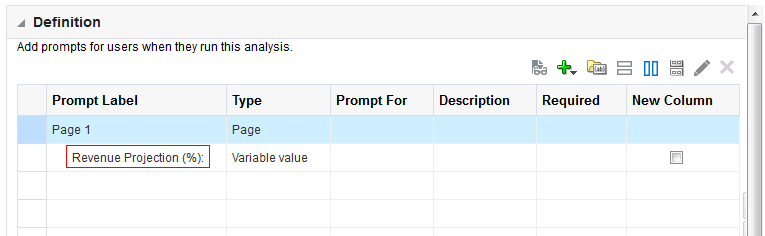
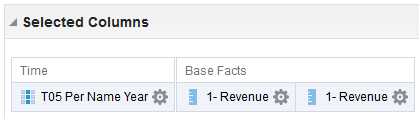
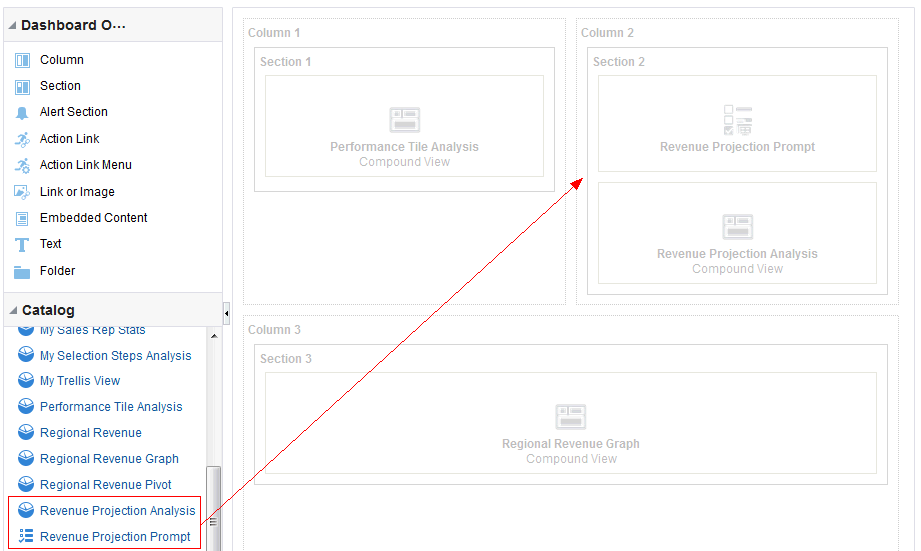
1)Write a query to display only friday dates from Jan, 2000 to till now?
SQL> SELECT SYSDATE,TO_CHAR(SYSDATE,'DY') FROM DUAL;
SYSDATE TO_
--------- ---
24-DEC-16 SAT
SELECT C_DATE,TO_CHAR(C_DATE,'DY') FROM
(
SELECT TO_DATE('01-JAN-2016','DD-MON-YYYY')+LEVEL-1 C_DATE FROM DUAL CONNECT BY LEVEL <=(SYSDATE - TO_DATE('01-JAN-2016','DD-MON-YYYY')+1)) WHERE TO_CHAR(C_DATE,'DY')='FRI';
2)EVERY day i am gettiing a file how to display jan 5th file in unix
ls -l | grep 'yyyy-mm-dd'ls -l | grep --color=auto '2006-01-05'
You can sort it as follows:
ls -lu | grep --color=auto '2006-01-05'
List ALL *.c File Accessed 30 Days Ago
Type the following command
find /home/you -iname "*.c" -atime -30 -type -f
3)difference bet rownum and rowid
rowid has a physical significance i.e you can read a row if you know rowid. It is complete physical address of a row.
While rownum is temporary serial number allocated to each returned row during query execution.
ROWID is a unique pseudo number assigned to a row.
Rownum returns the number of rows for a resultant query. BOTH are pseudo columns not occupying any physical space in the database.
Example of Rownum:
Sort salary and return first 5 rows.
select * from
( select *
from emp
order by sal desc )
where ROWNUM <= 5;
Example of Rowid:
Below query selects address of all rows that contain data for students in department 20
SELECT ROWID, last_name
FROM student
WHERE department_id = 20;
RowId represents a row in a table internally. It can be used for fast access to the row. Rownum is a function of the result set.
select * from Student where rownum = 2 will get the first 2 rows of your result set.
INFORMATICA - Target Update Override : Updating Target
Table without any Primary Keys defined.
http://ramakantshankar.blogspot.in/2014/03/informatica-target-update-override.html
UDATE
SET = :TU.
WHERE = :TU.
AND [other conditions]
- Example:
UPDATE EMPL_POST_HIST
SET POST = :TU.POST
, UPDATE_DATE = :TU.UPDATE_DATE
WHERE EMPL = :TU.EMPL
4 ways to delete duplicate records Oracle
1. Using rowid
SQL > delete from emp
where rowid not in
(select max(rowid) from emp group by empno);
This technique can be applied to almost scenarios. Group by operation should be on the columns which identify the duplicates.
2. Using self-join
SQL > delete from emp e1
where rowid not in
(select max(rowid) from emp e2
where e1.empno = e2.empno );
3. Using row_number()
SQL > delete from emp where rowid in
(
select rid from
(
select rowid rid,
row_number() over(partition by empno order by empno) rn
from emp
)
where rn > 1
);
This is another efficient way to delete duplicates
4. Using dense_rank()
SQL > delete from emp where rowid in
(
select rid from
(
select rowid rid,
dense_rank() over(partition by empno order by rowid) rn
from emp
)
where rn > 1
);
Here you can use both rank() and dens_rank() since both will give unique records when order by rowid.
USING UNIX:-
$ sort file | uniq
$ sort -u file
What is an Inline View?INLINE VIEW
It is not a schema object like a normal view.
It is sub query with a name (alias) placed in the from clause of another select statement (main query) for which it (the sub query) acts as a data source.
The outer query will have a reference of the inline view.
The inline view can have a GROUP BY clause, order by clause or even inline view itself can be join.
Inline views are useful for performing the Top-N (Top 3 sales reps or top 10 students etc) analysis.
See AN EXAMPLE OF INLINE VIEW, WHICH HAS THE GROUP BY CLAUSE. The query finds the employees in the emp table whose salary is less than the maximum salary of their department.
SQL> SELECT ENAME,SAL,E1.DEPTNO,E2.MAXSAL FROM EMP E1,
(SELECT DEPTNO,MAX(SAL) MAXSAL FROM EMP GROUP BY DEPTNO)E2
WHERE E1.DEPTNO=E2.DEPTNO AND E1.SAL
ENAME SAL DEPTNO MAXSAL
---------- ---------- ---------- ----------
CLARK 2450 10 5000
MILLER 1300 10 5000
SMITH 800 20 3000
ADAMS 1100 20 3000
JONES 2975 20 3000
ALLEN 1600 30 2850
MARTIN 1250 30 2850
JAMES 950 30 2850
TURNER 1500 30 2850
WARD 1250 30 2850
10 rows selected.
SELECT ENAME,SAL,E1.DEPTNO,E2.MAXSAL FROM EMP E1,
(SELECT DEPTNO,MAX(SAL) MAXSAL FROM EMP GROUP BY DEPTNO order by deptno)E2 WHERE E1.DEPTNO=E2.DEPTNO AND E1.SAL
ENAME SAL DEPTNO MAXSAL
---------- ---------- ---------- ----------
CLARK 2450 10 5000
MILLER 1300 10 5000
SMITH 800 20 3000
ADAMS 1100 20 3000
JONES 2975 20 3000
ALLEN 1600 30 2850
MARTIN 1250 30 2850
JAMES 950 30 2850
TURNER 1500 30 2850
WARD 1250 30 2850
10 rows selected.
display max 3rd salary in oracle:-
select * from (select * from (select ename,sal from emp order by sal desc)
where rownum < 4 order by sal)
where rownum = 1;
SELECT name, salary FROM #Employee e1 WHERE 3-1 = (SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT salary) FROM #Employee e2 WHERE e2.salary > e1.salary);
Solution to finding the 2nd highest salary in SQL
SELECT MAX(Salary) FROM Employee
WHERE Salary NOT IN (SELECT MAX(Salary) FROM Employee )
SET
WHERE
AND [other conditions]
4 ways to delete duplicate records Oracle
1. Using rowid
SQL > delete from emp
where rowid not in
(select max(rowid) from emp group by empno);
where rowid not in
(select max(rowid) from emp group by empno);
This technique can be applied to almost scenarios. Group by operation should be on the columns which identify the duplicates.
2. Using self-join
SQL > delete from emp e1
where rowid not in
(select max(rowid) from emp e2
where e1.empno = e2.empno );
where rowid not in
(select max(rowid) from emp e2
where e1.empno = e2.empno );
3. Using row_number()
SQL > delete from emp where rowid in
(
select rid from
(
select rowid rid,
row_number() over(partition by empno order by empno) rn
from emp
)
where rn > 1
);
(
select rid from
(
select rowid rid,
row_number() over(partition by empno order by empno) rn
from emp
)
where rn > 1
);
This is another efficient way to delete duplicates
4. Using dense_rank()
SQL > delete from emp where rowid in
(
select rid from
(
select rowid rid,
dense_rank() over(partition by empno order by rowid) rn
from emp
)
where rn > 1
);
(
select rid from
(
select rowid rid,
dense_rank() over(partition by empno order by rowid) rn
from emp
)
where rn > 1
);
Here you can use both rank() and dens_rank() since both will give unique records when order by rowid.
USING UNIX:-
$ sort file | uniq
$ sort -u file
What is an Inline View?INLINE VIEW
It is not a schema object like a normal view.It is sub query with a name (alias) placed in the from clause of another select statement (main query) for which it (the sub query) acts as a data source.
The outer query will have a reference of the inline view.
The inline view can have a GROUP BY clause, order by clause or even inline view itself can be join.
Inline views are useful for performing the Top-N (Top 3 sales reps or top 10 students etc) analysis.
See AN EXAMPLE OF INLINE VIEW, WHICH HAS THE GROUP BY CLAUSE. The query finds the employees in the emp table whose salary is less than the maximum salary of their department.
SQL> SELECT ENAME,SAL,E1.DEPTNO,E2.MAXSAL FROM EMP E1,
(SELECT DEPTNO,MAX(SAL) MAXSAL FROM EMP GROUP BY DEPTNO)E2
WHERE E1.DEPTNO=E2.DEPTNO AND E1.SAL
ENAME SAL DEPTNO MAXSAL
---------- ---------- ---------- ----------
CLARK 2450 10 5000
MILLER 1300 10 5000
SMITH 800 20 3000
ADAMS 1100 20 3000
JONES 2975 20 3000
ALLEN 1600 30 2850
MARTIN 1250 30 2850
JAMES 950 30 2850
TURNER 1500 30 2850
WARD 1250 30 2850
10 rows selected.
SELECT ENAME,SAL,E1.DEPTNO,E2.MAXSAL FROM EMP E1,
(SELECT DEPTNO,MAX(SAL) MAXSAL FROM EMP GROUP BY DEPTNO order by deptno)E2 WHERE E1.DEPTNO=E2.DEPTNO AND E1.SAL
ENAME SAL DEPTNO MAXSAL
---------- ---------- ---------- ----------
CLARK 2450 10 5000
MILLER 1300 10 5000
SMITH 800 20 3000
ADAMS 1100 20 3000
JONES 2975 20 3000
ALLEN 1600 30 2850
MARTIN 1250 30 2850
JAMES 950 30 2850
TURNER 1500 30 2850
WARD 1250 30 2850
10 rows selected.
display max 3rd salary in oracle:-
select * from (select * from (select ename,sal from emp order by sal desc)
where rownum < 4 order by sal)
where rownum = 1;
SELECT name, salary FROM #Employee e1 WHERE 3-1 = (SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT salary) FROM #Employee e2 WHERE e2.salary > e1.salary);
Solution to finding the 2nd highest salary in SQL
SELECT MAX(Salary) FROM Employee
WHERE Salary NOT IN (SELECT MAX(Salary) FROM Employee )




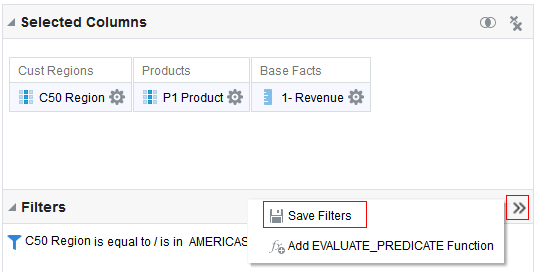
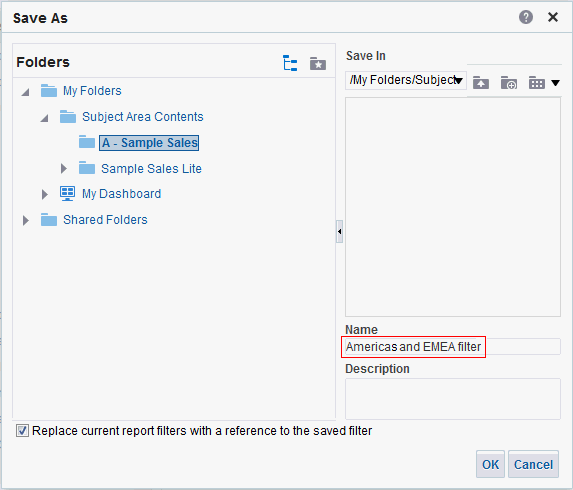
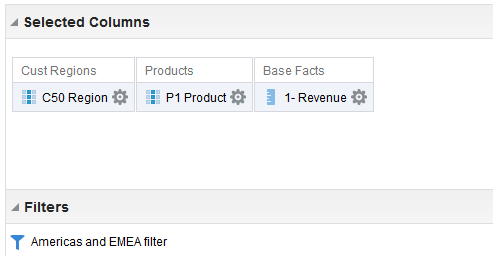
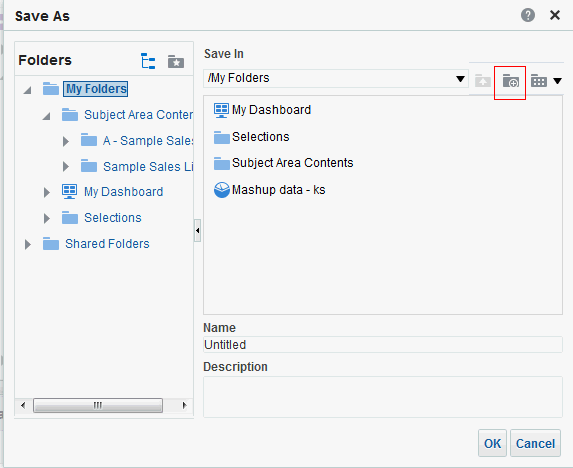
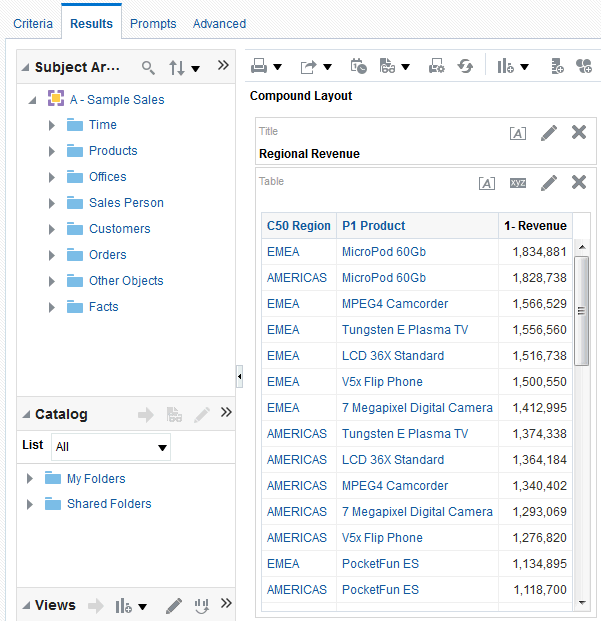
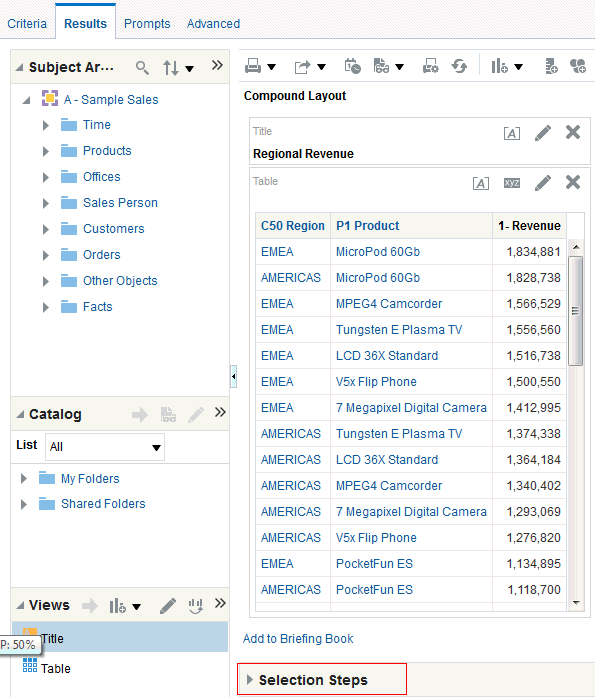
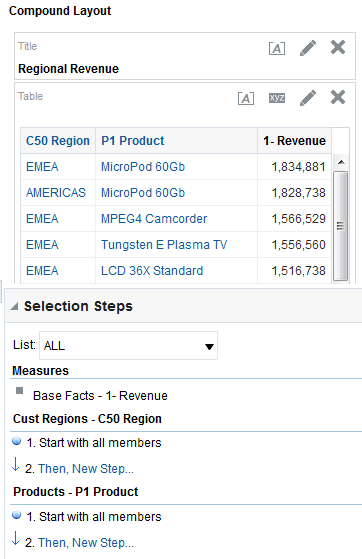
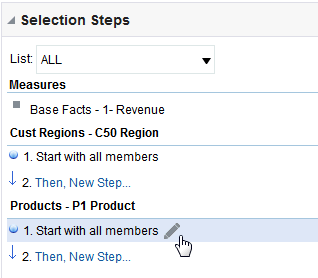
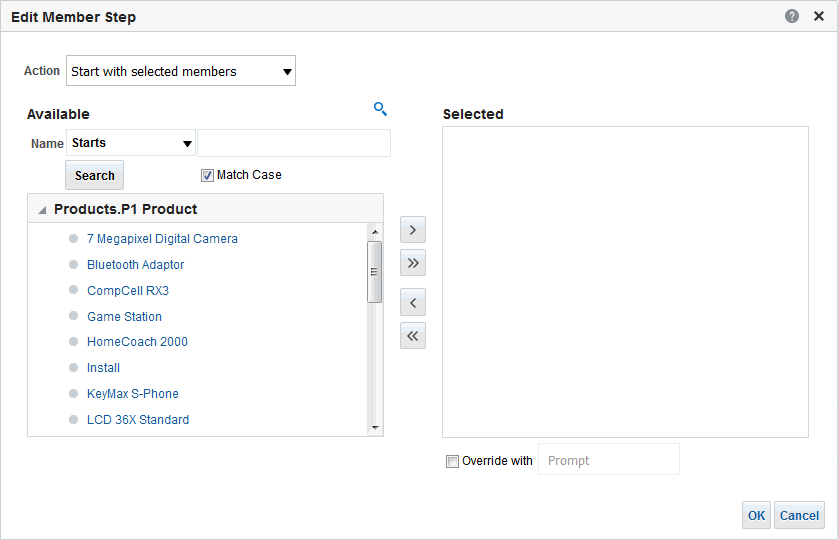

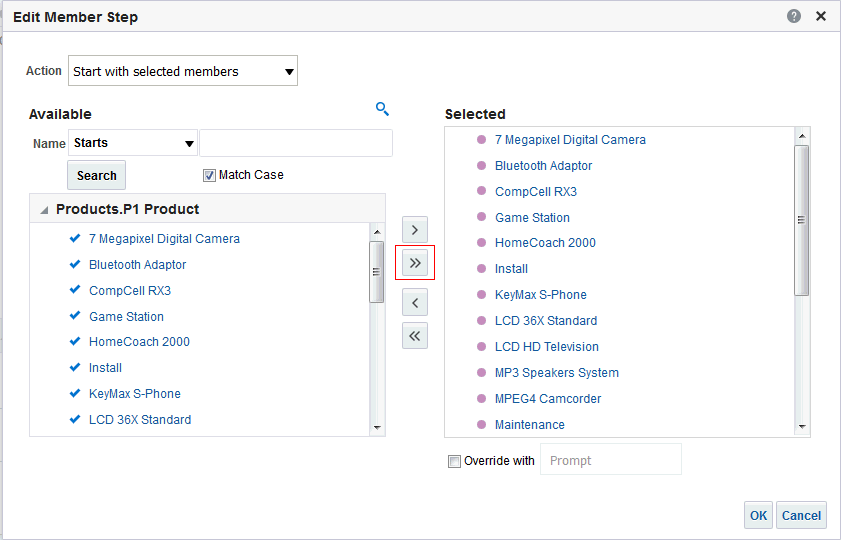
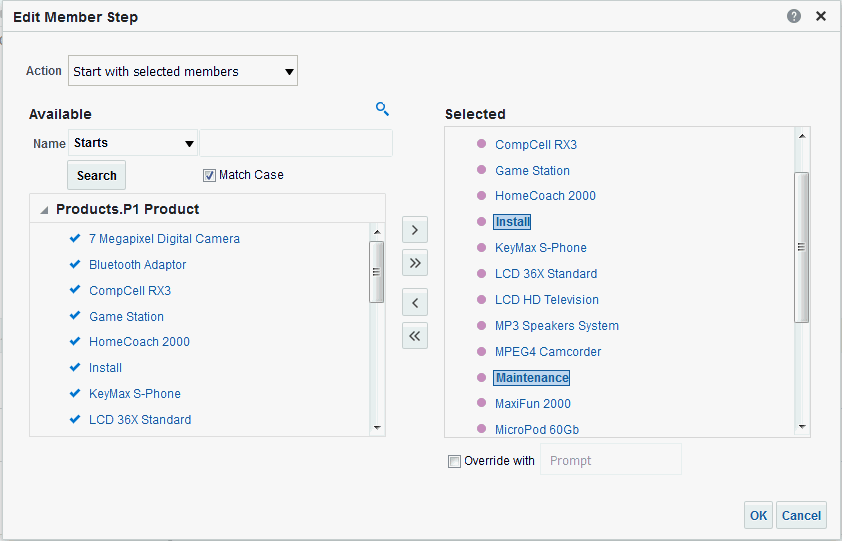
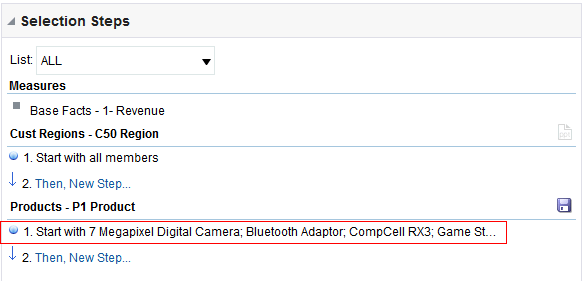

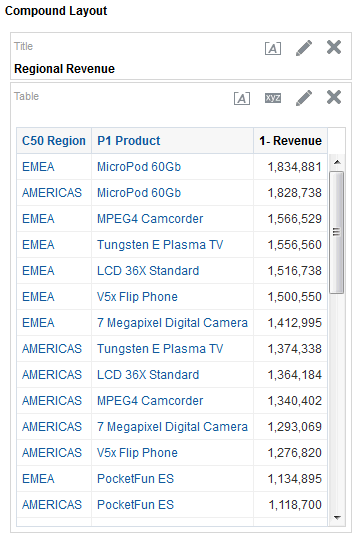
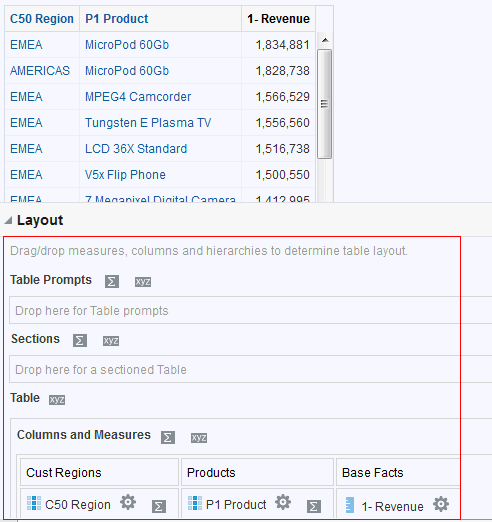
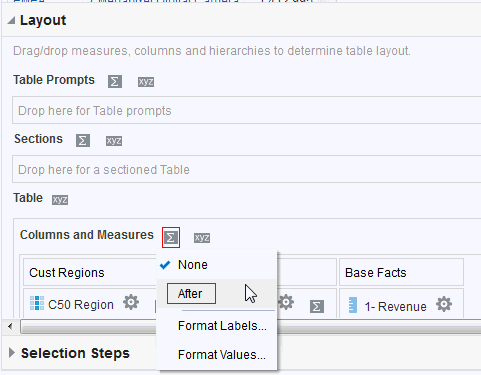
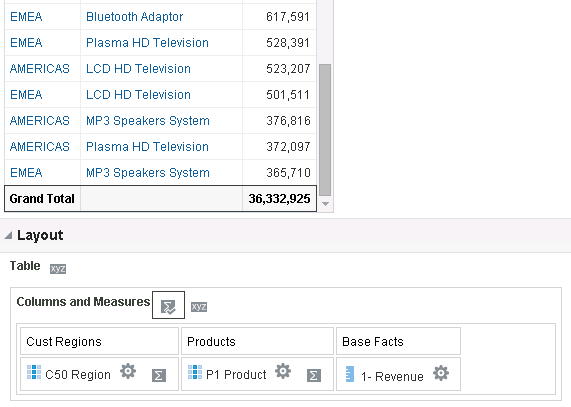

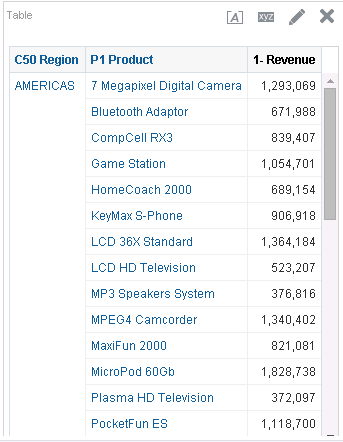
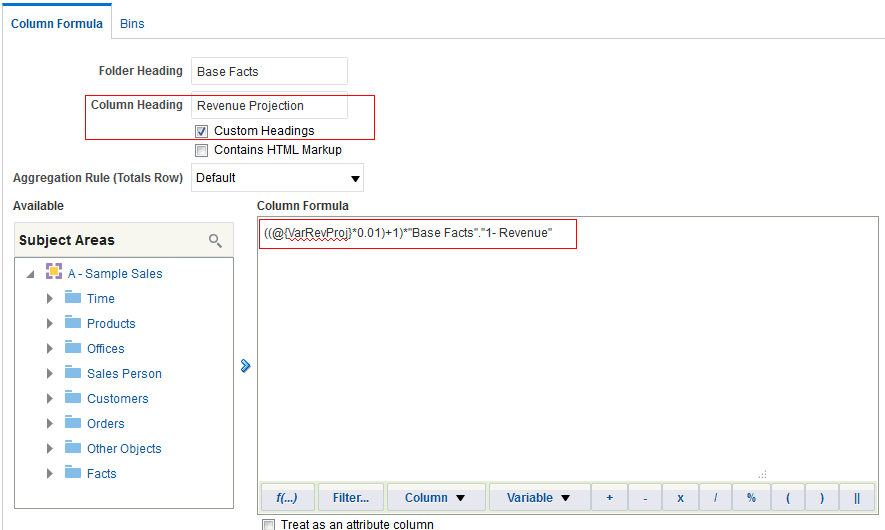
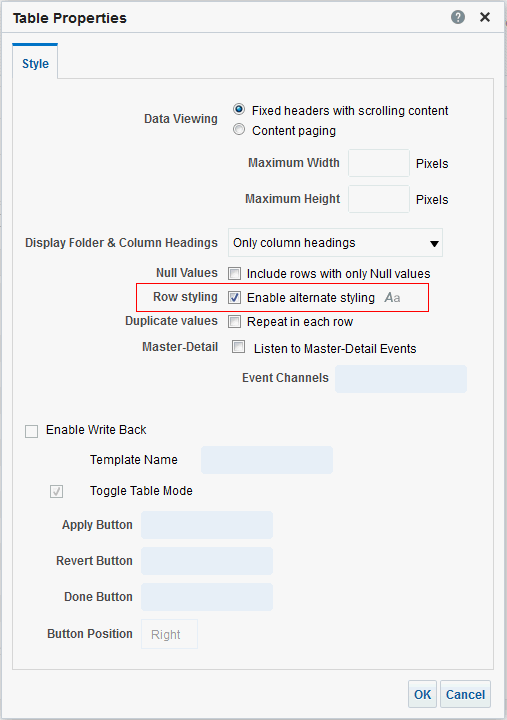
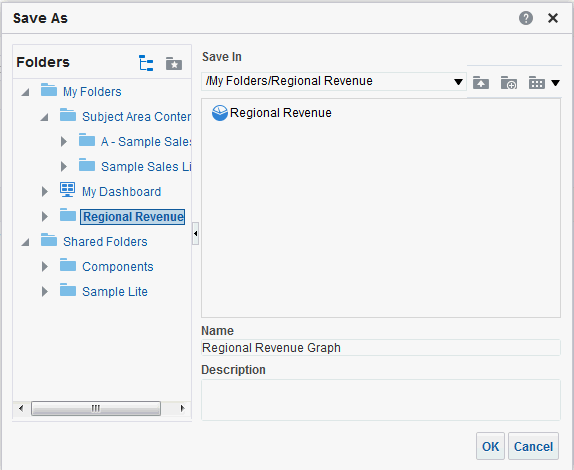
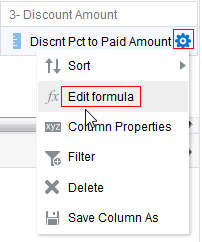
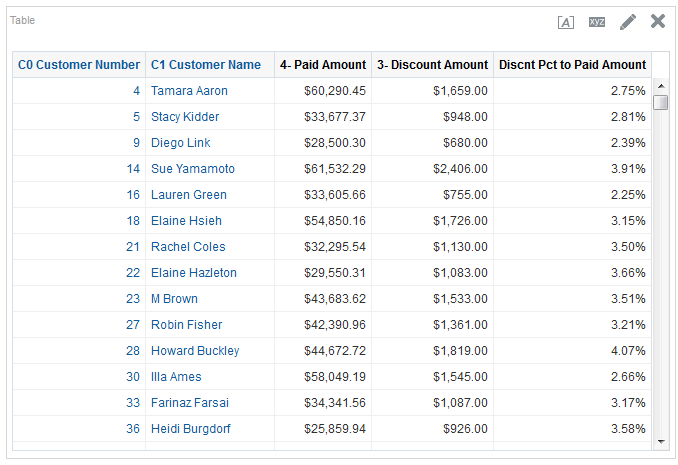
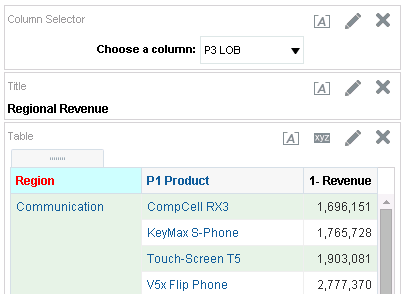
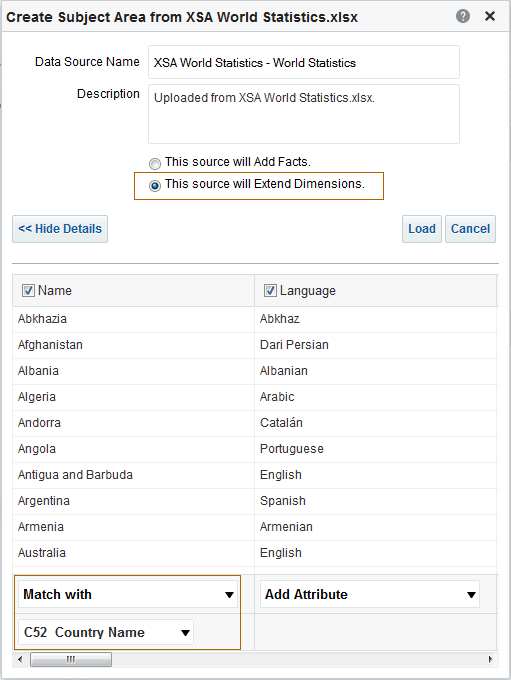
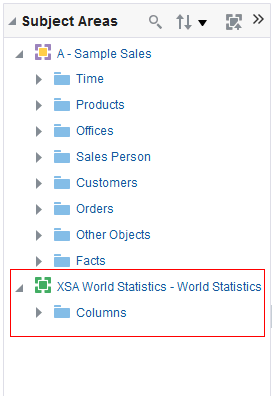
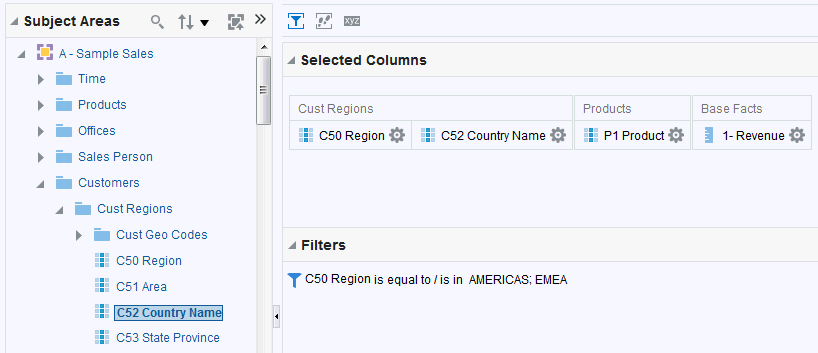
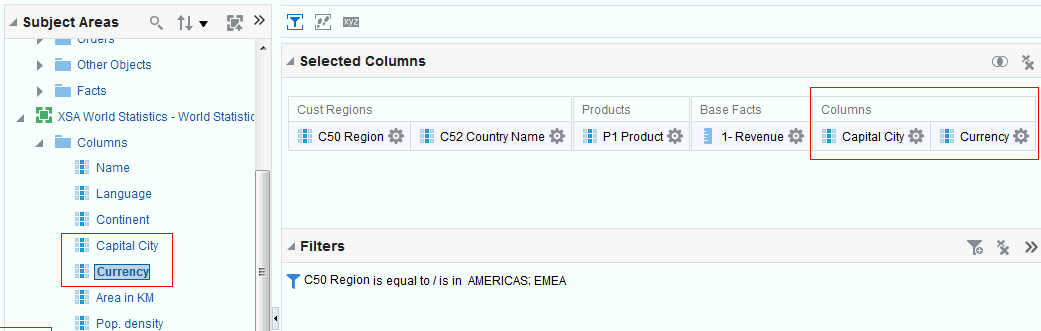
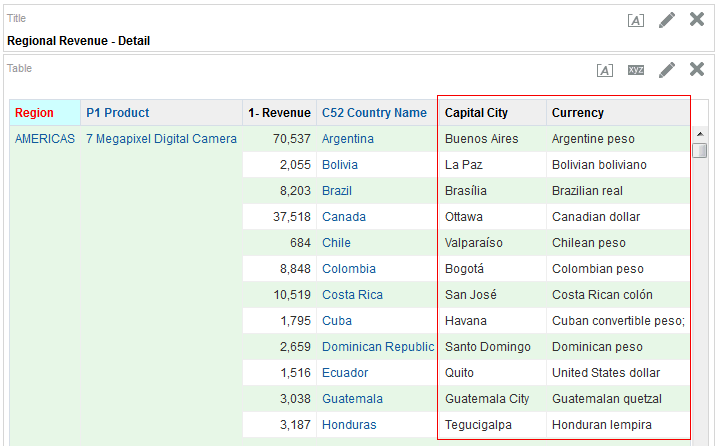
 in the Table view. The Table Editor appears.
in the Table view. The Table Editor appears.
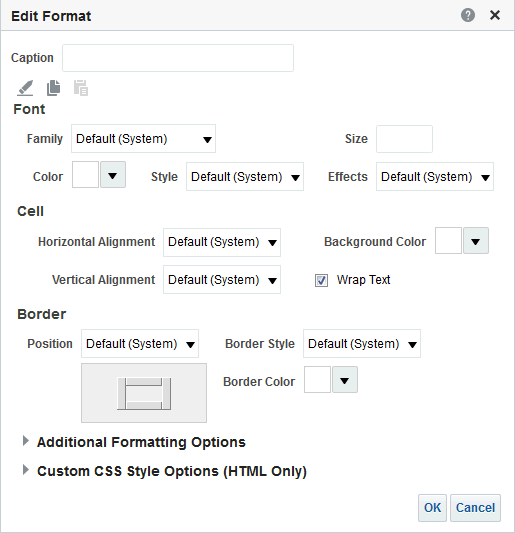
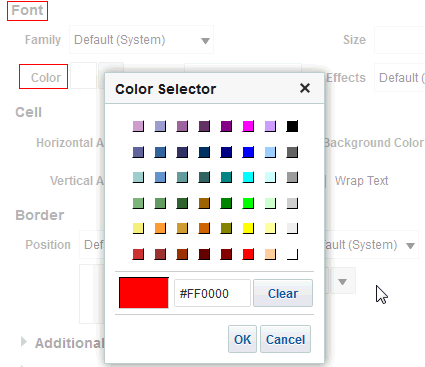
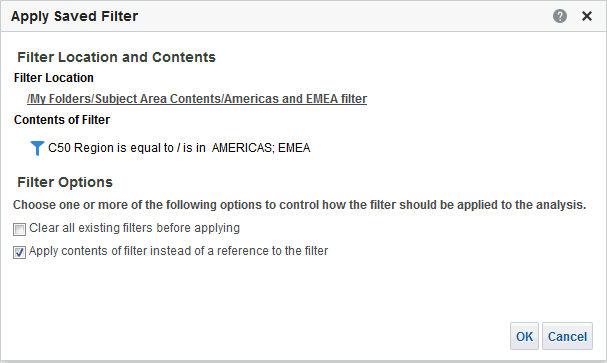
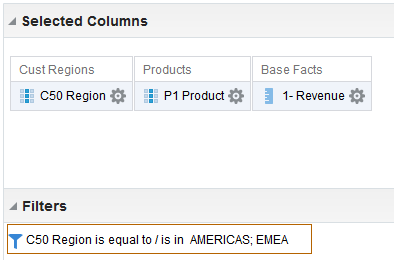
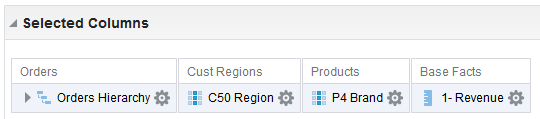
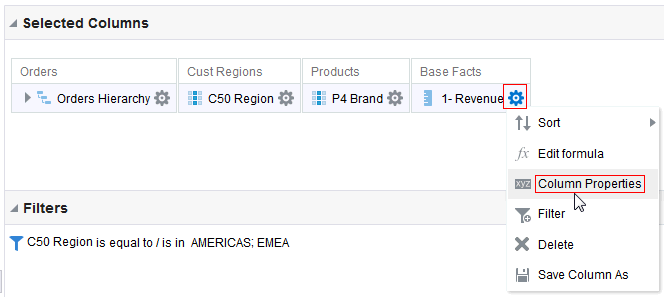
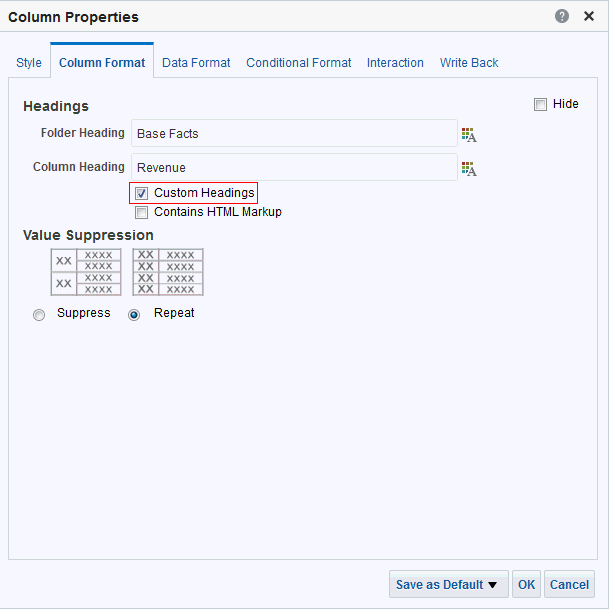
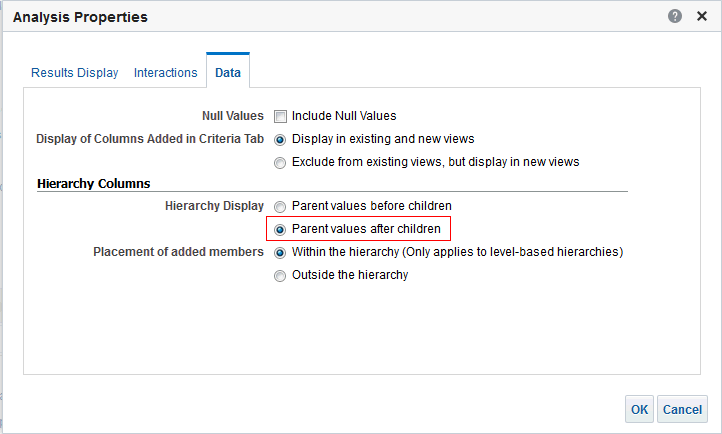
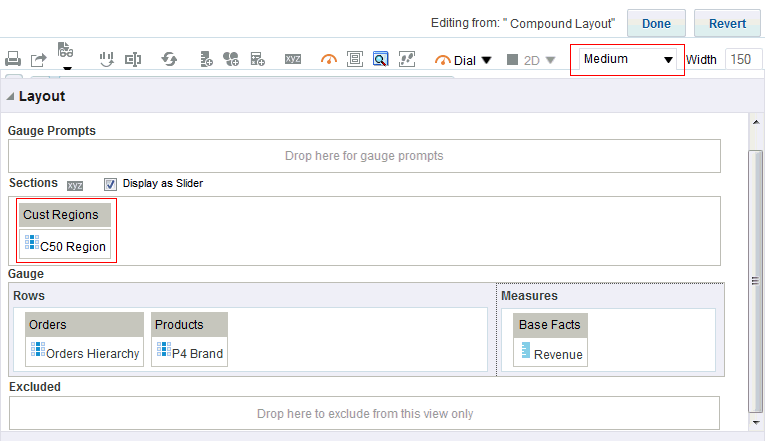
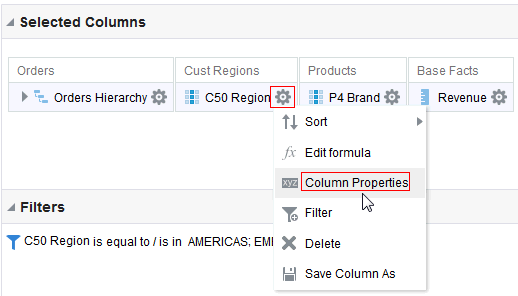
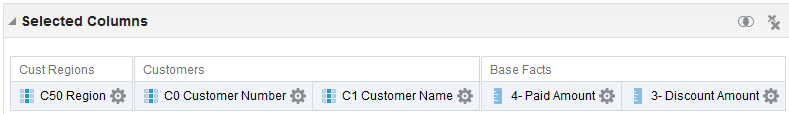
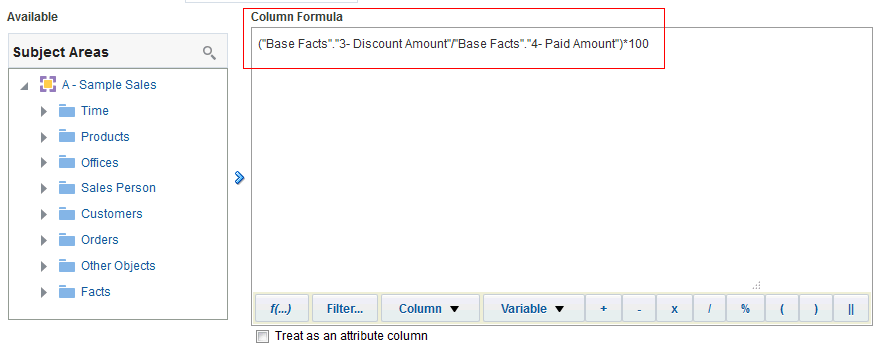
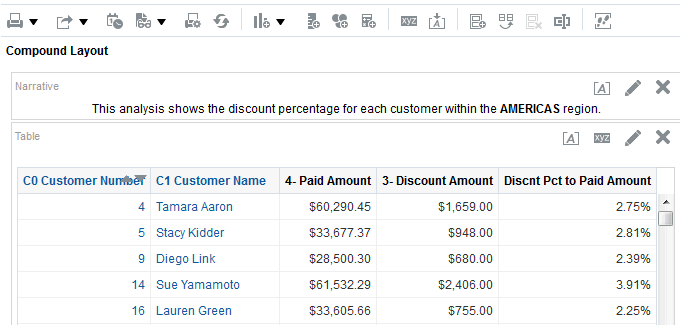
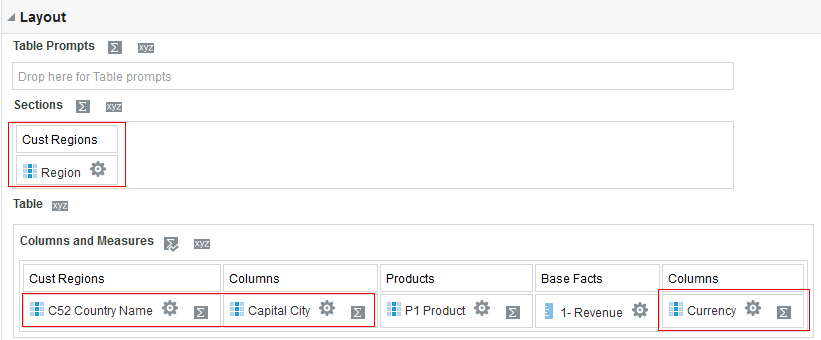
 for C50 Region and select Format Headings.
for C50 Region and select Format Headings.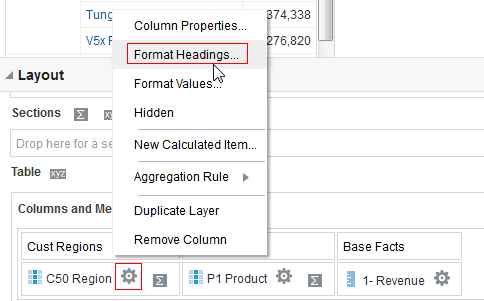
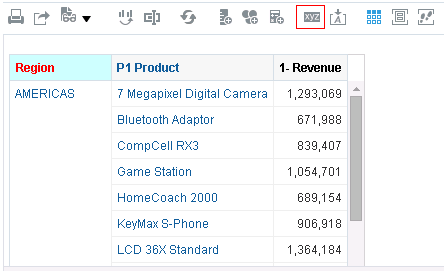
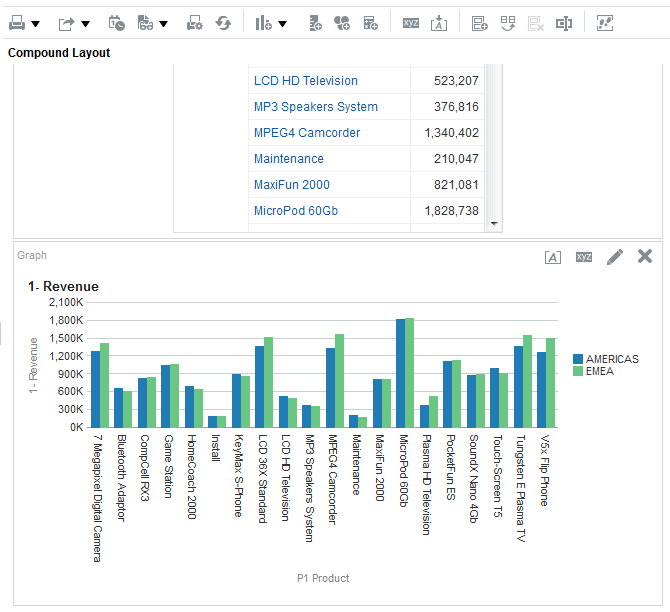

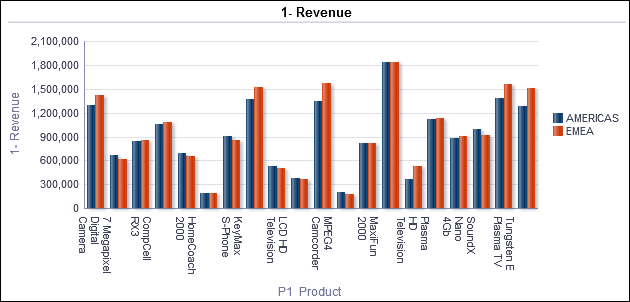
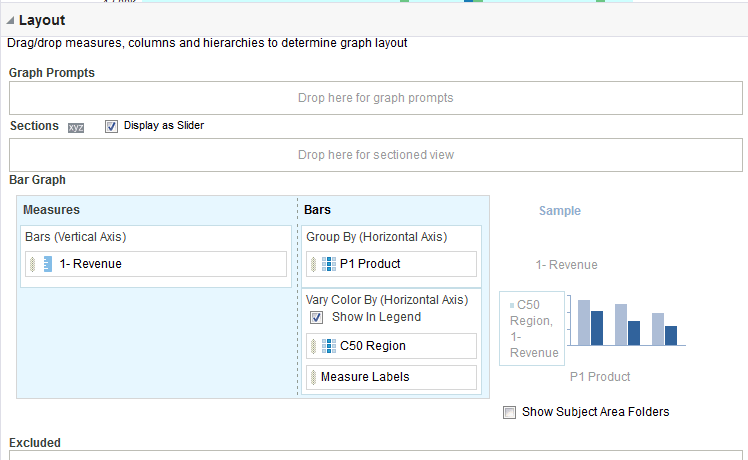
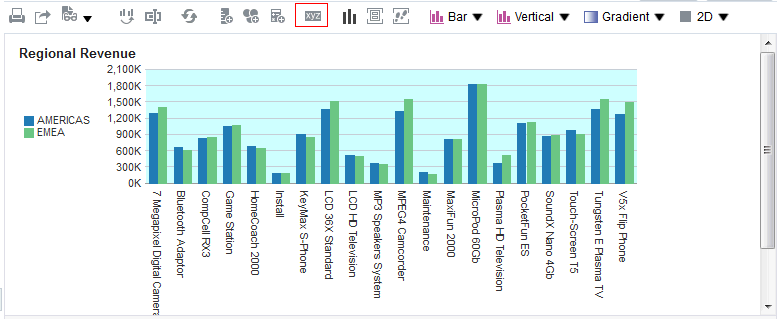
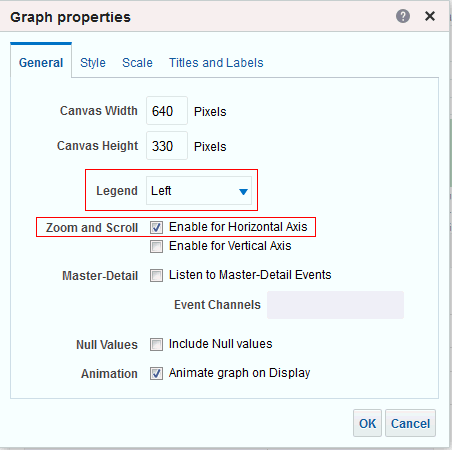


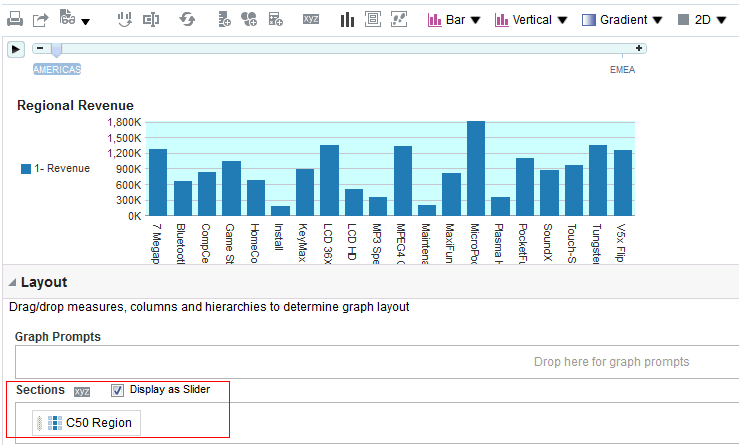
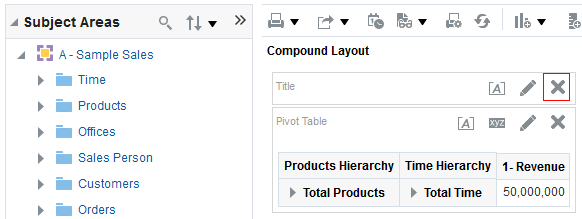
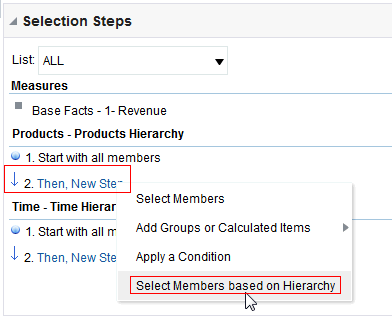

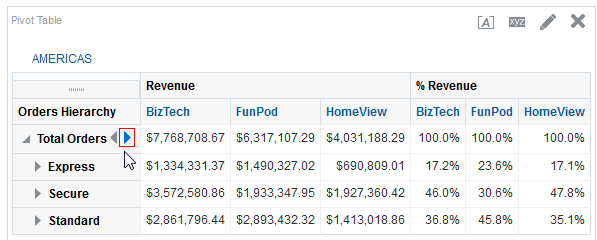
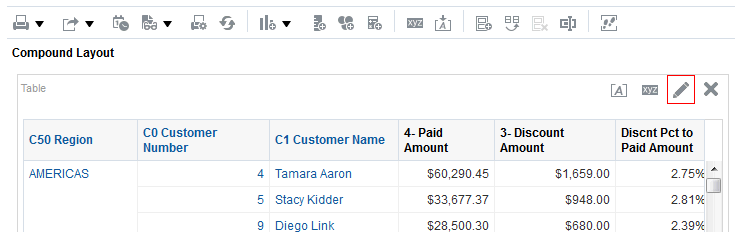
 icon to expand Total Orders.
icon to expand Total Orders.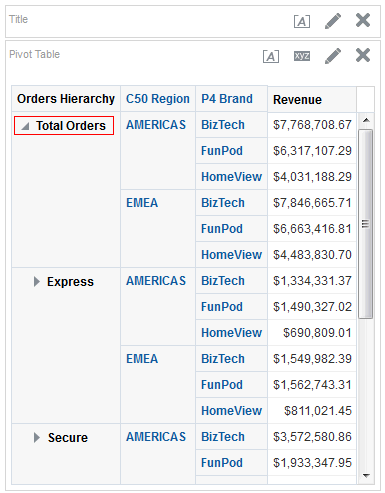
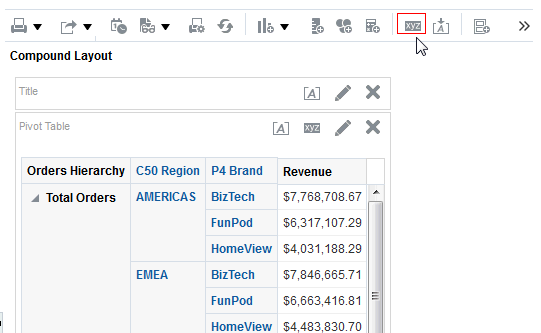

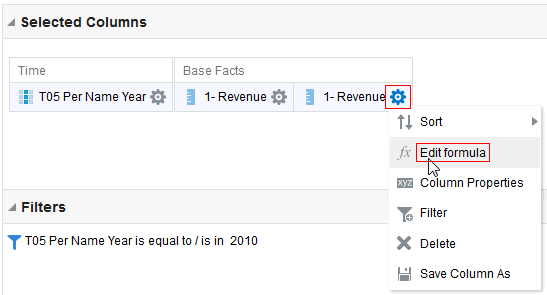
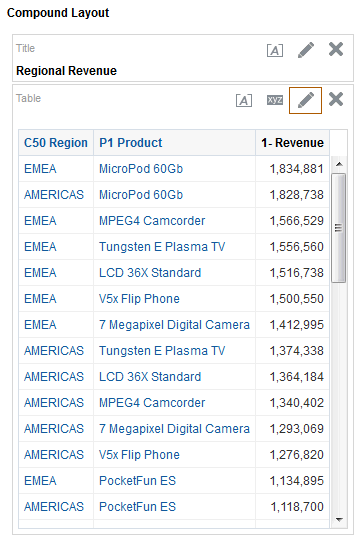
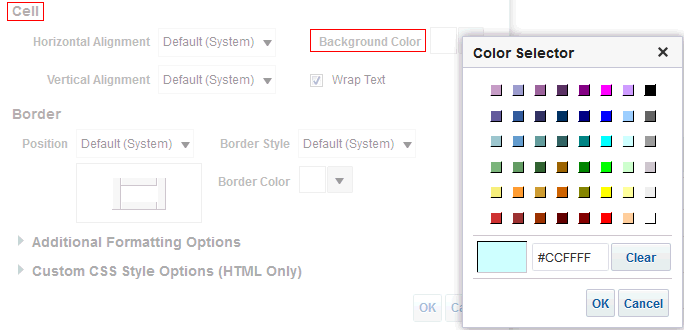
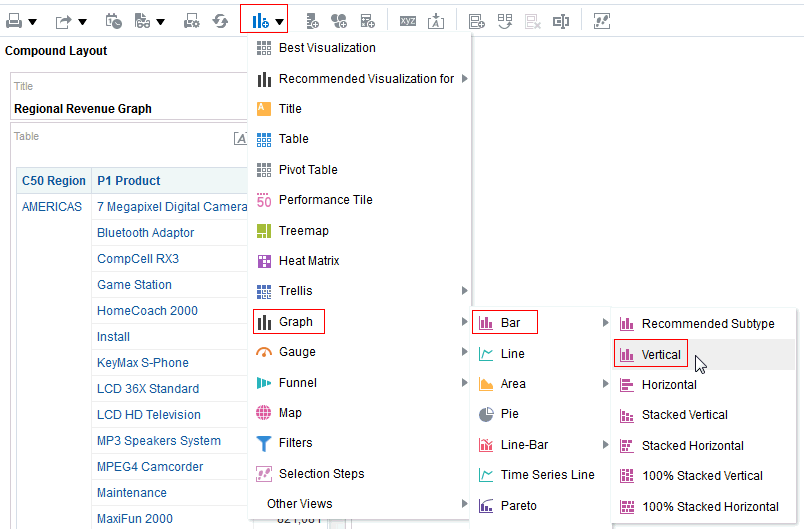
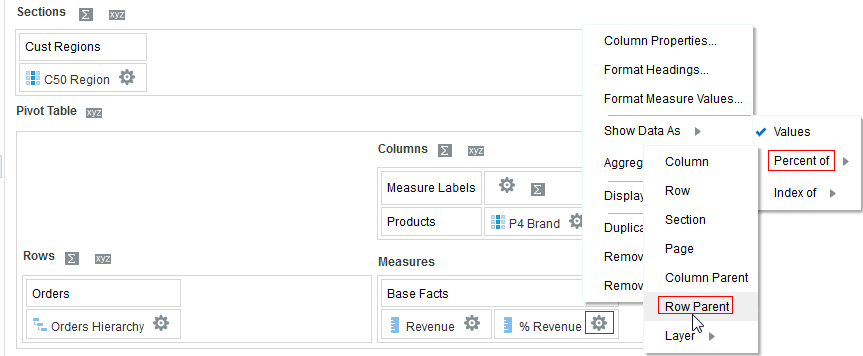
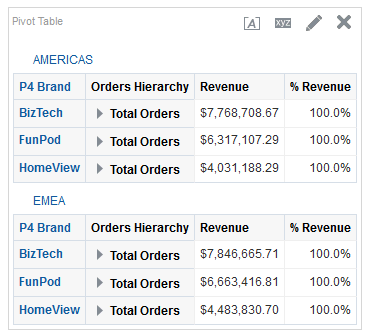
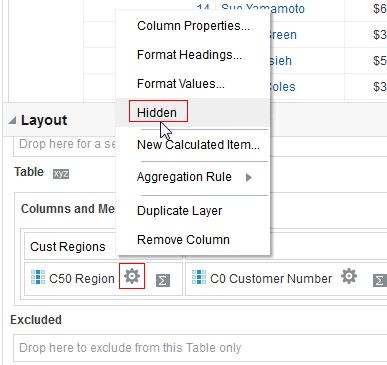
 for the Revenue column and selectDuplicate Layer.
for the Revenue column and selectDuplicate Layer.

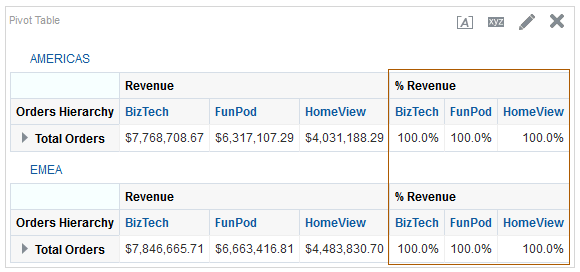
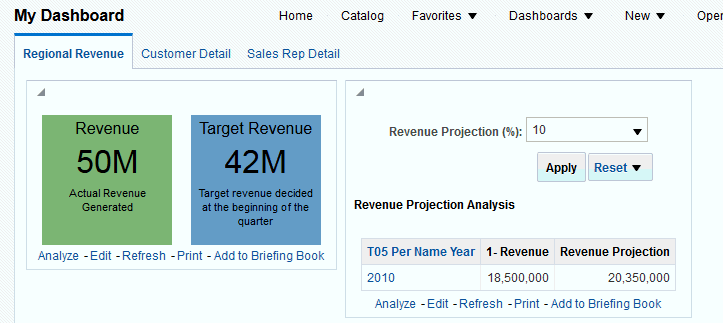
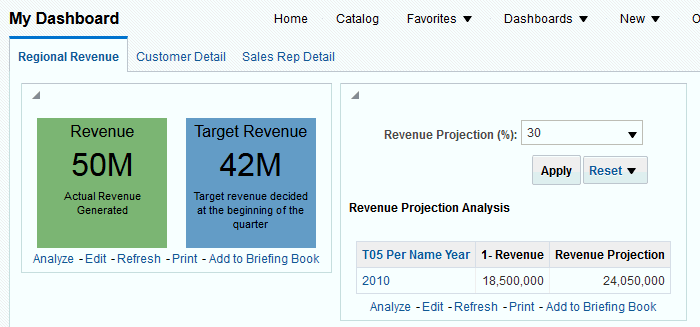
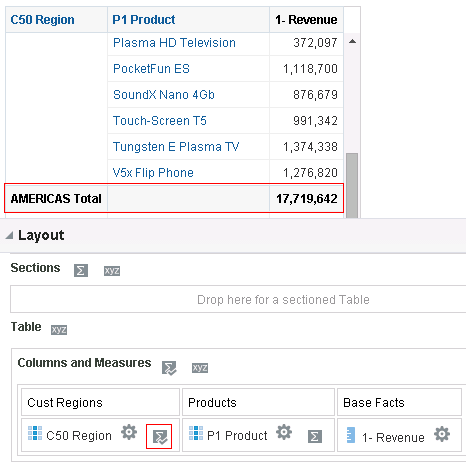
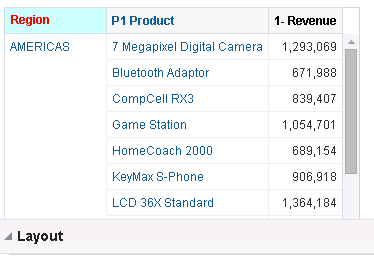
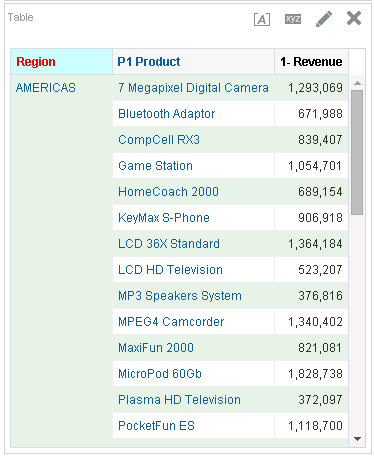
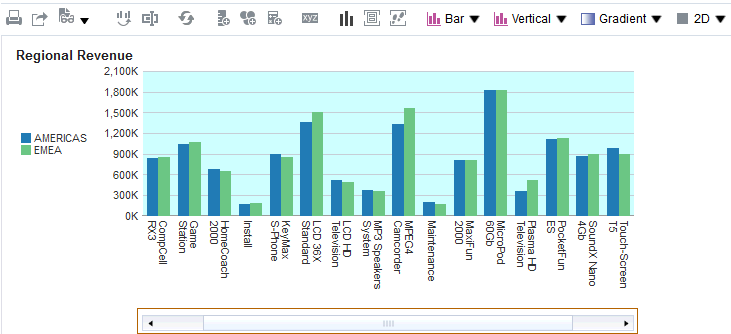
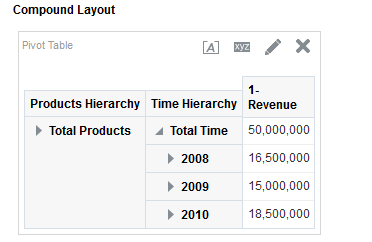
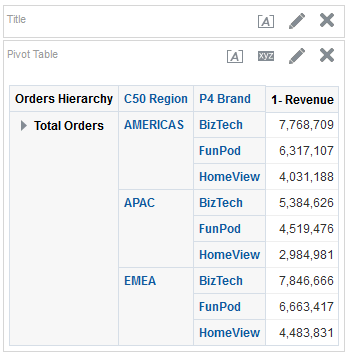
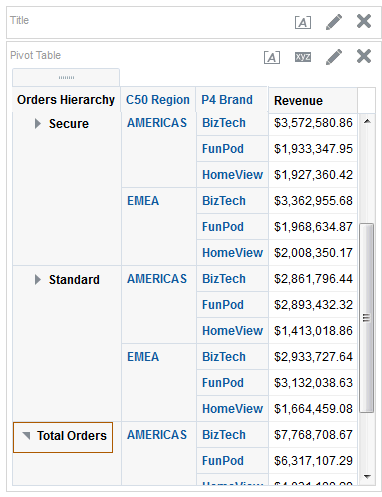
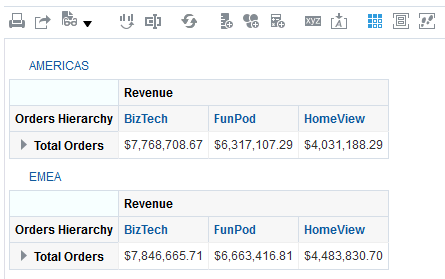
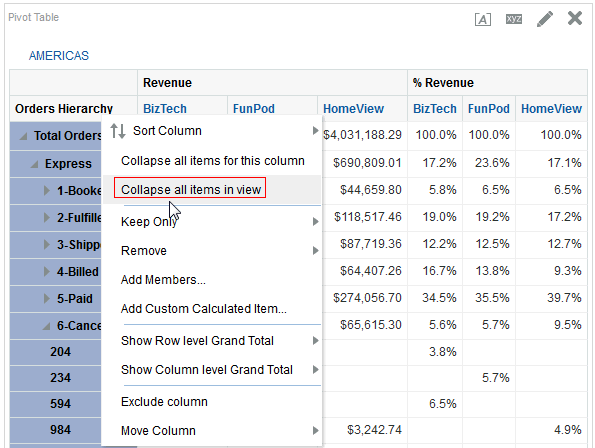
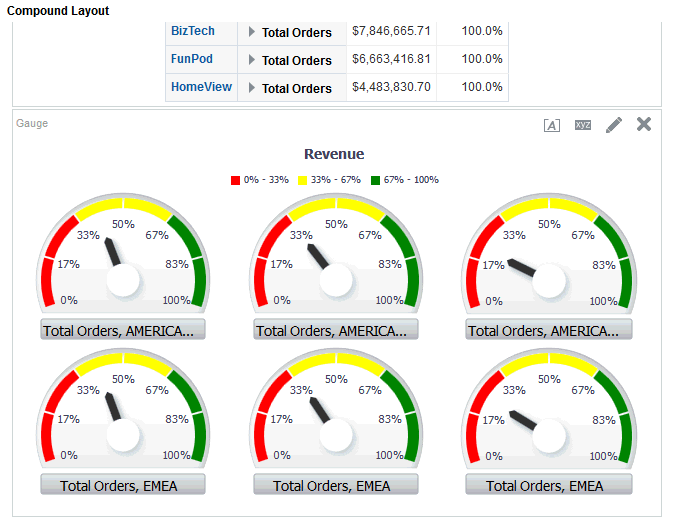
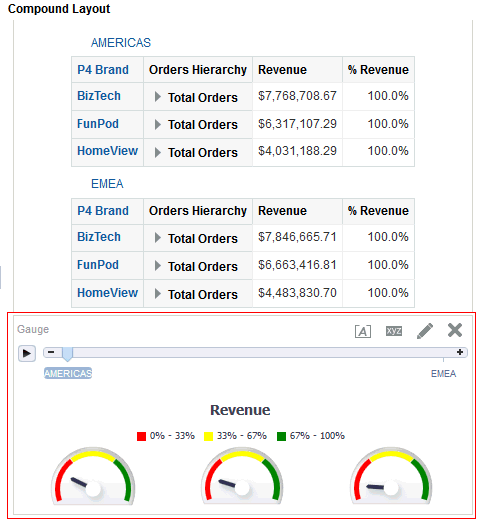
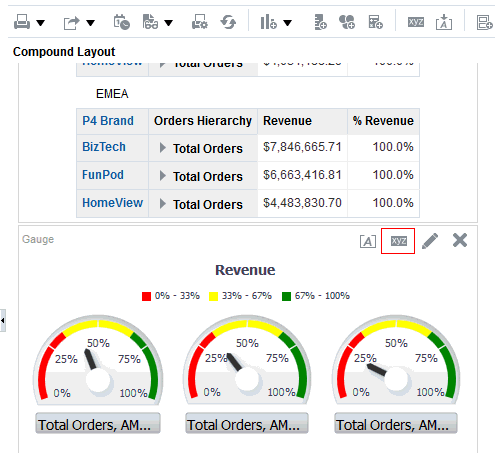
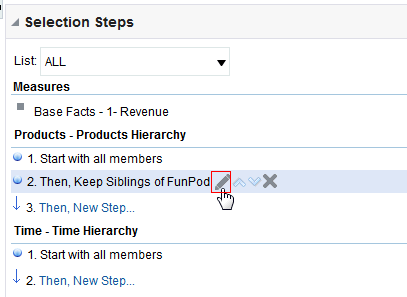
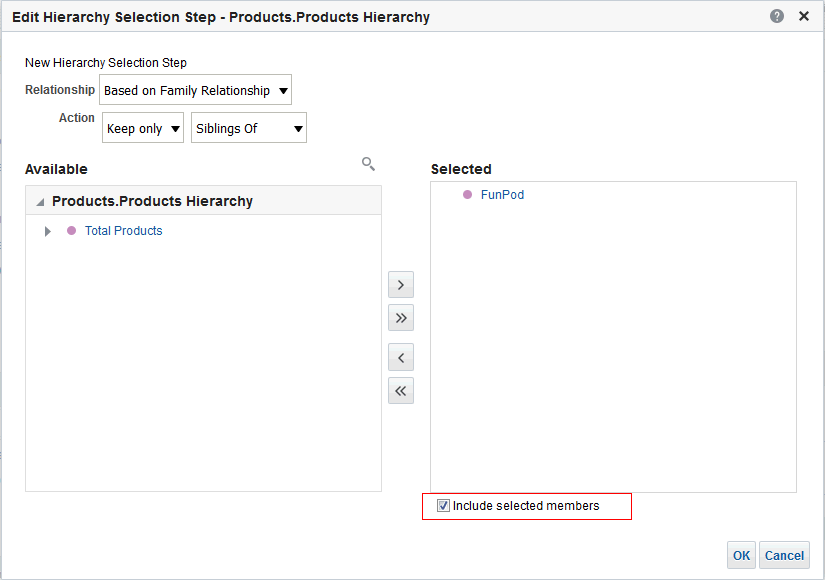
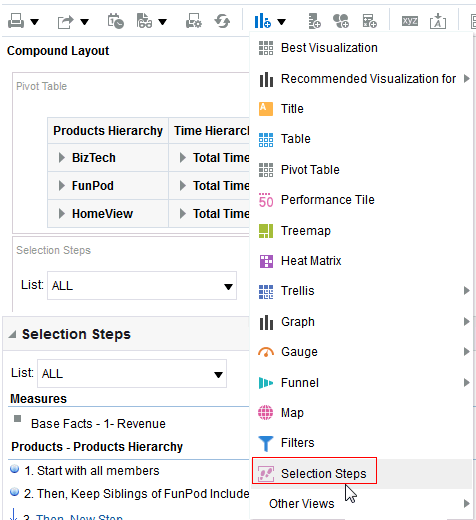
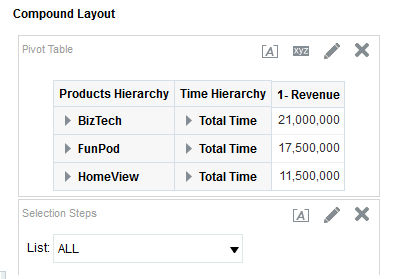
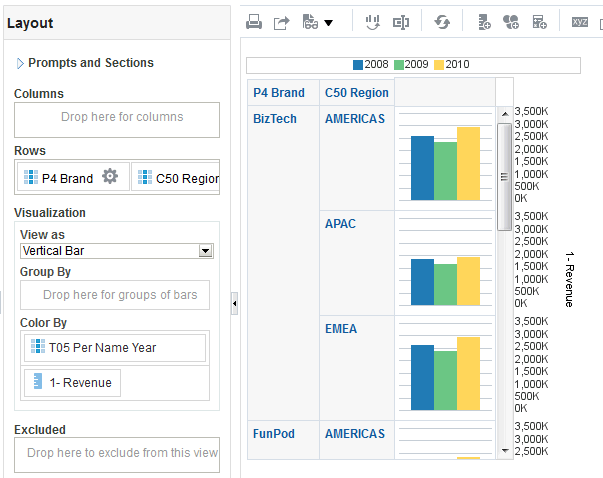
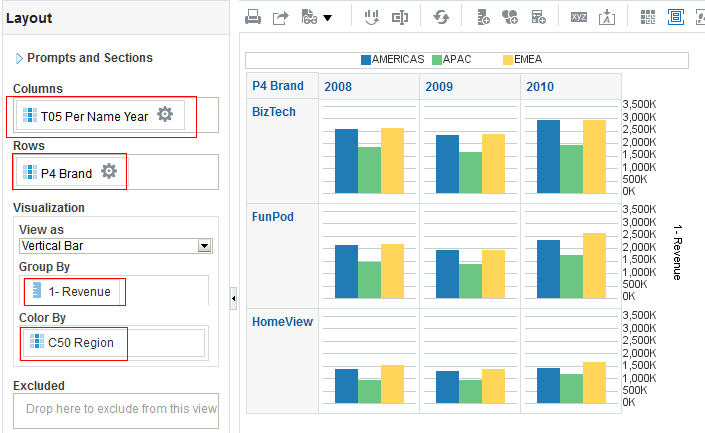
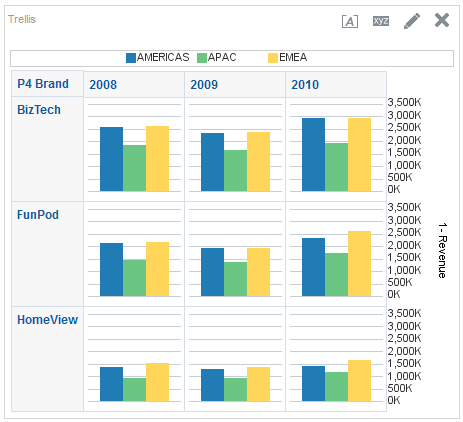
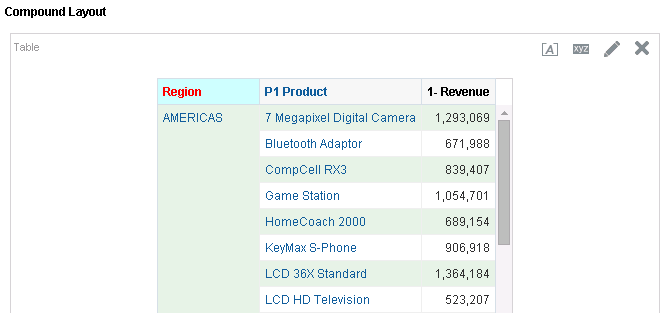
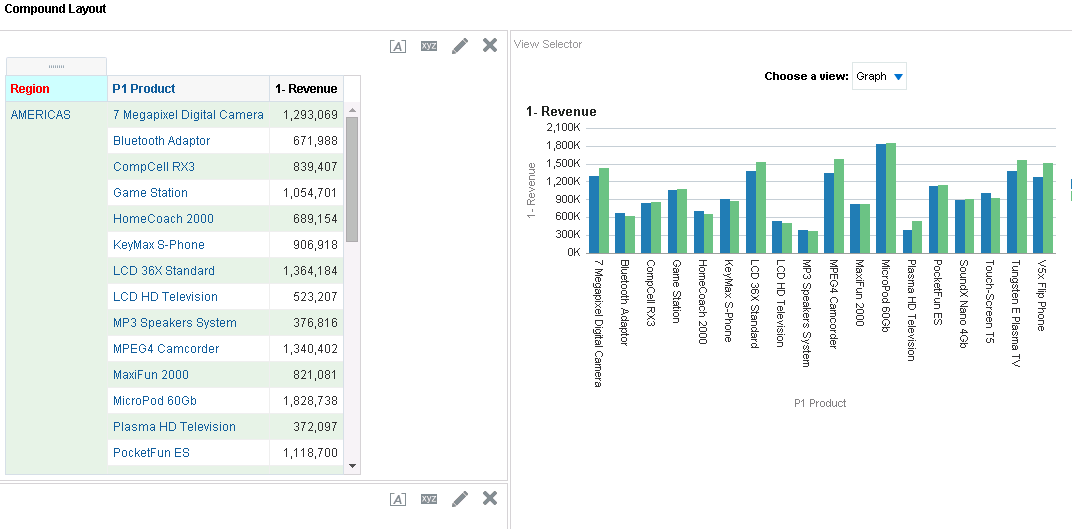
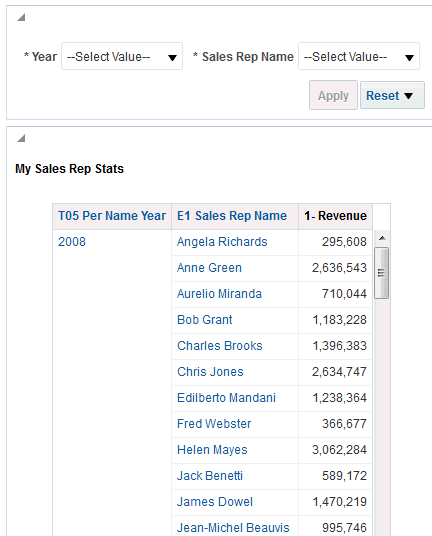
 for Total Orders for the Americas. The carat icons are used to expand and collapse the data for analysis. The Orders Hierarchy contains Orders on the row edge and Total Orders as the parent. Revenue is the measure.
for Total Orders for the Americas. The carat icons are used to expand and collapse the data for analysis. The Orders Hierarchy contains Orders on the row edge and Total Orders as the parent. Revenue is the measure.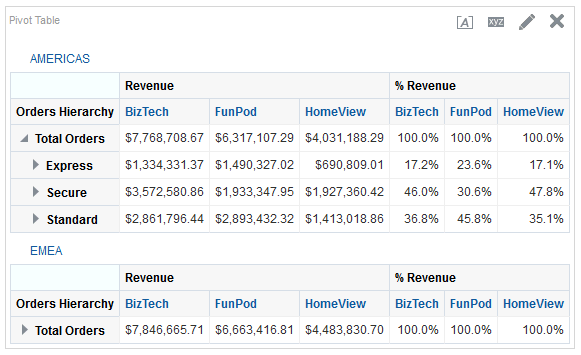

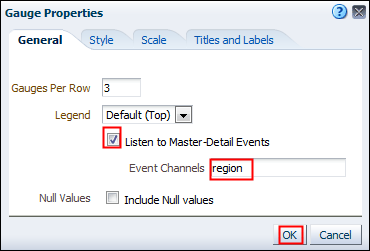

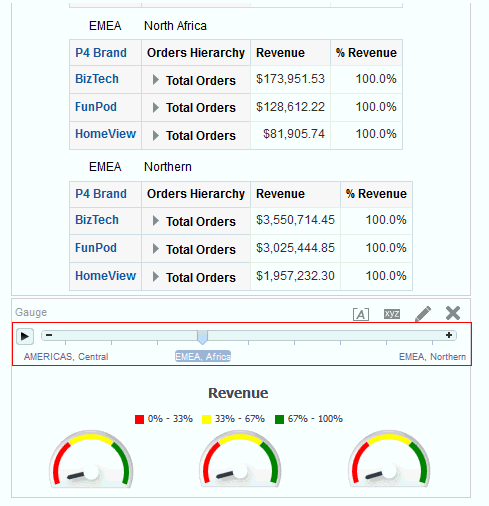
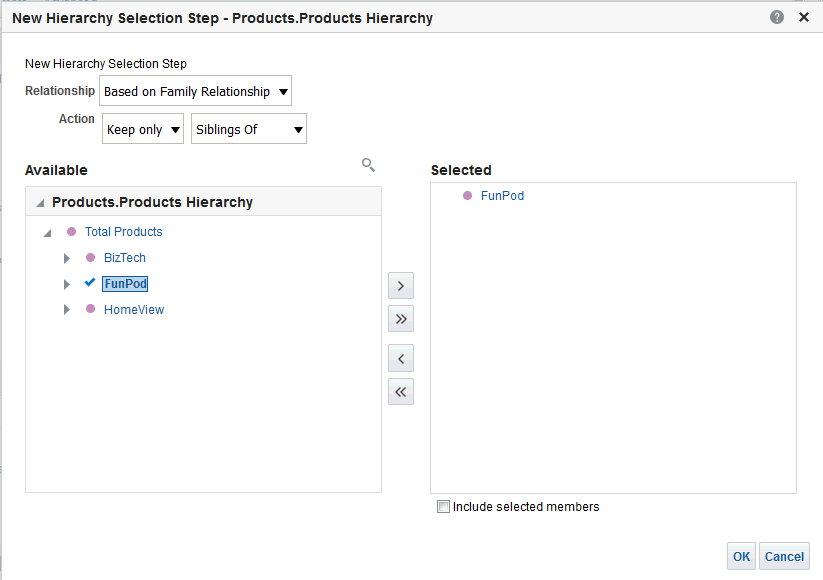
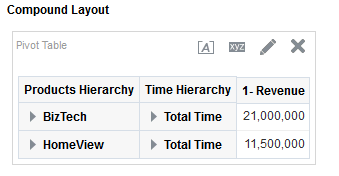
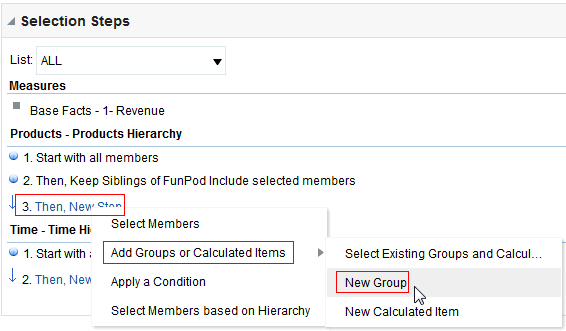
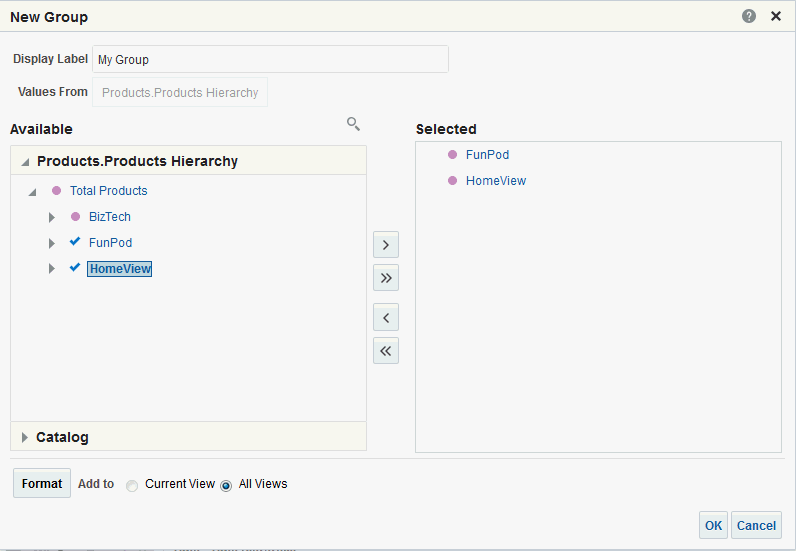

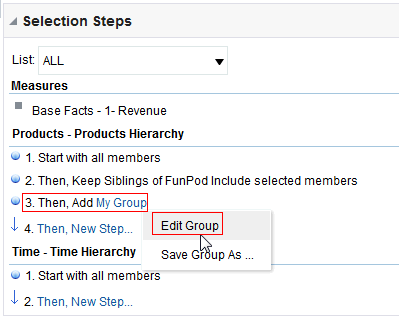
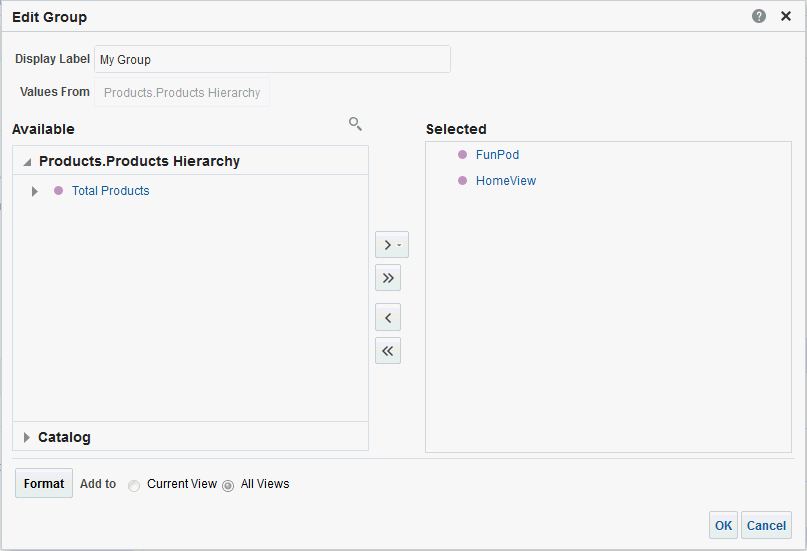
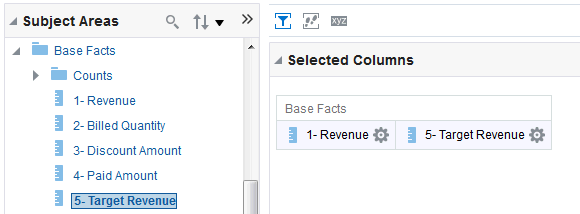
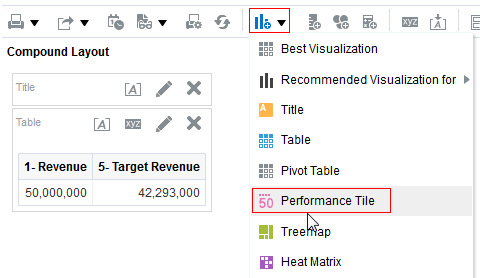

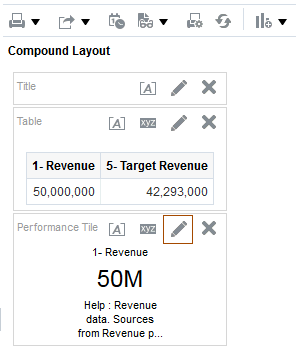

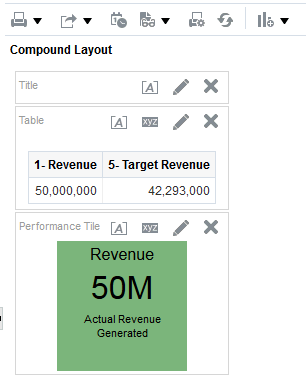



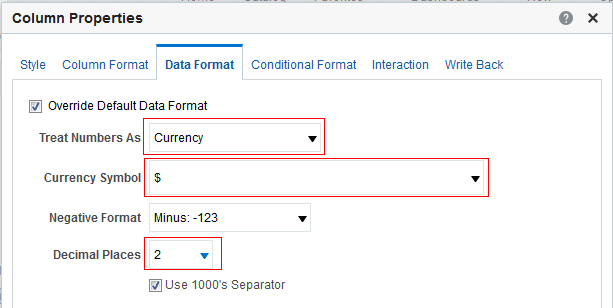
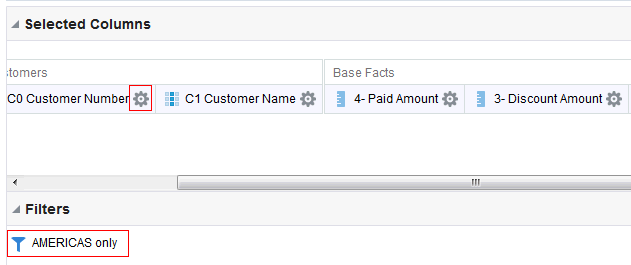
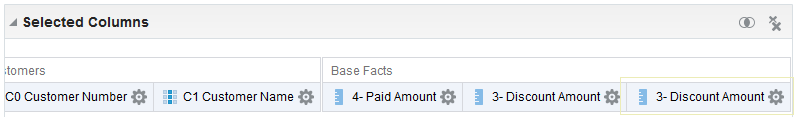
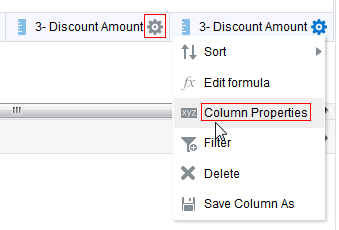



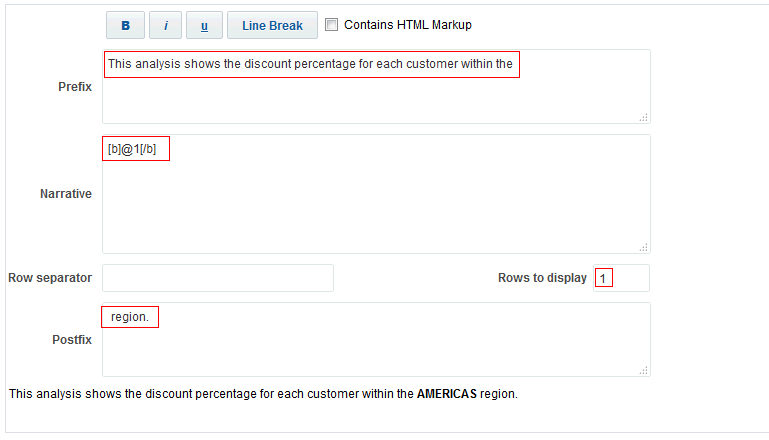










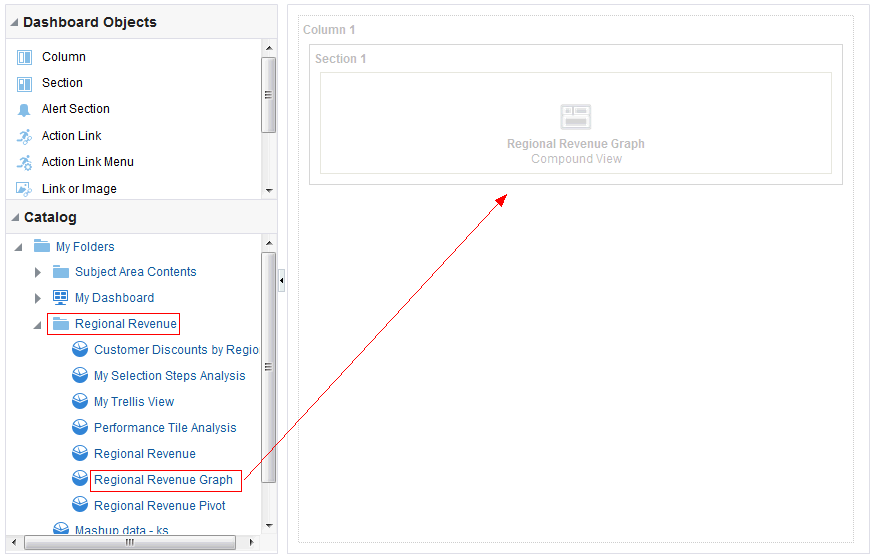
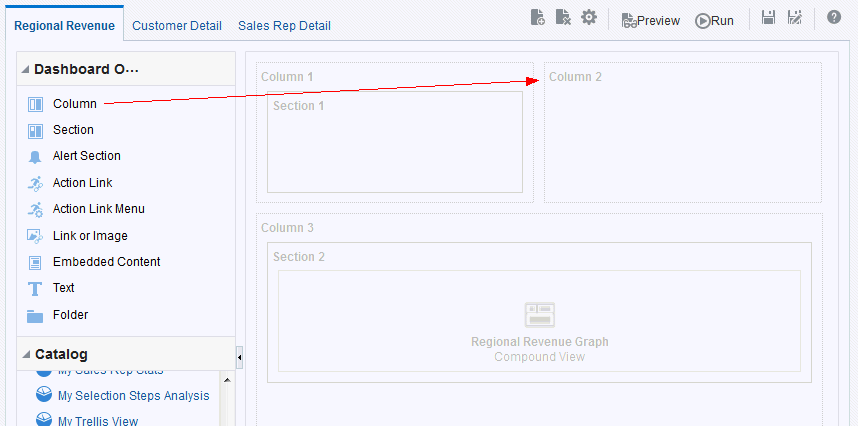
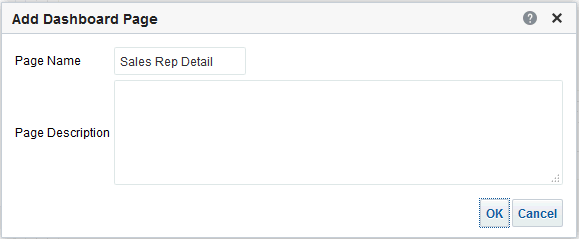
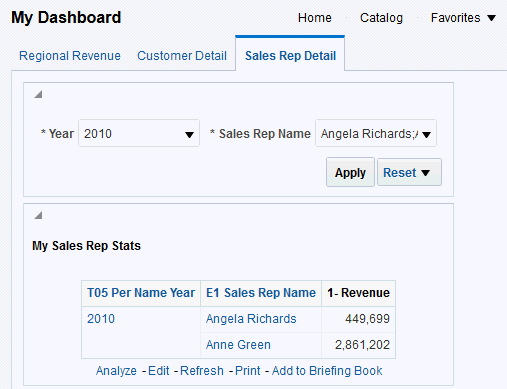
 ) to save the dashboard page and then click Run
) to save the dashboard page and then click Run  .
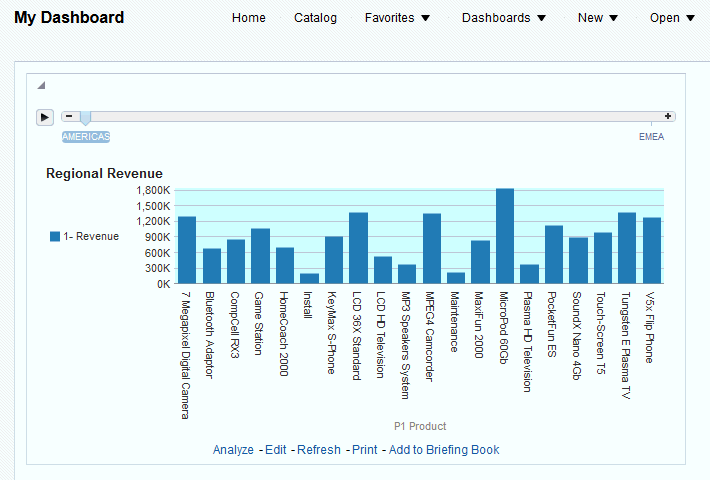
.
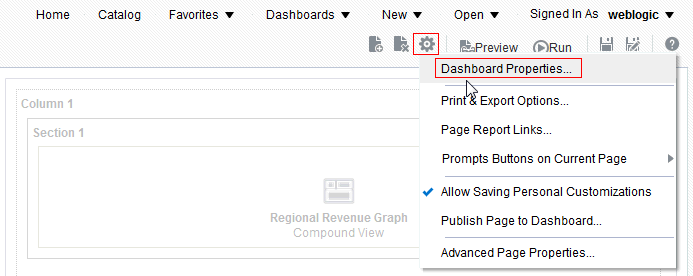
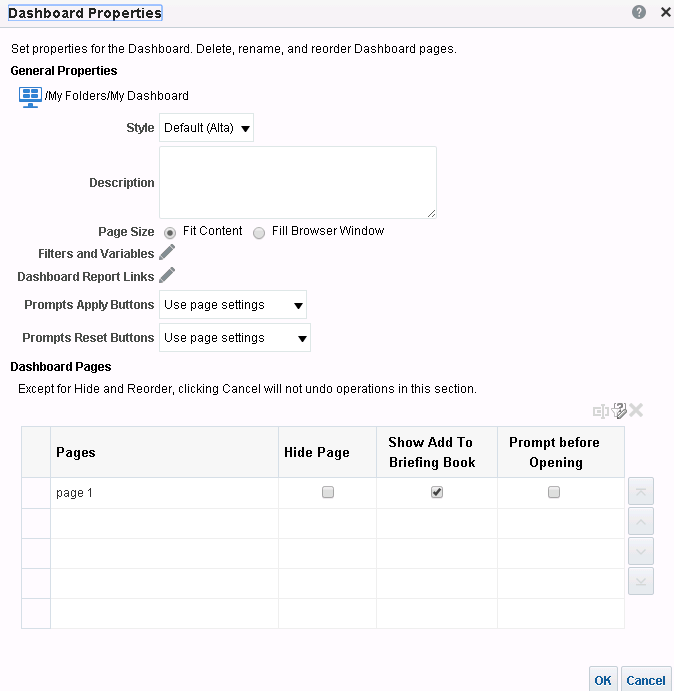







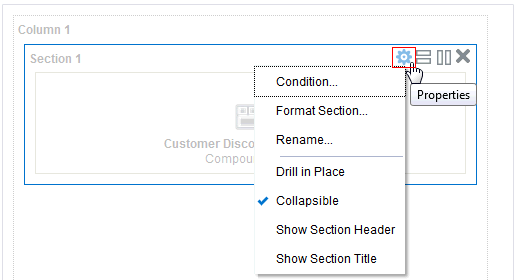
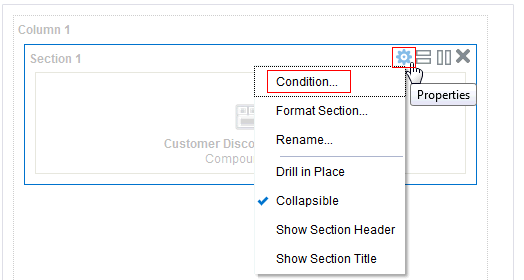
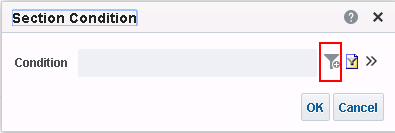
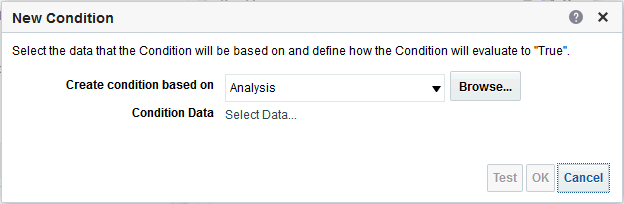
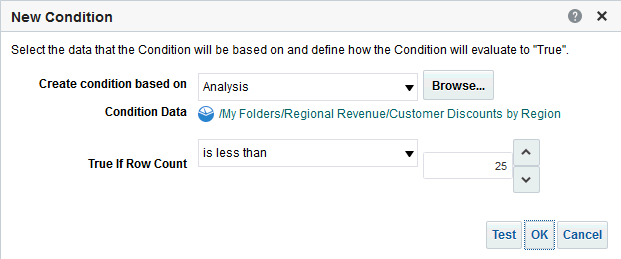
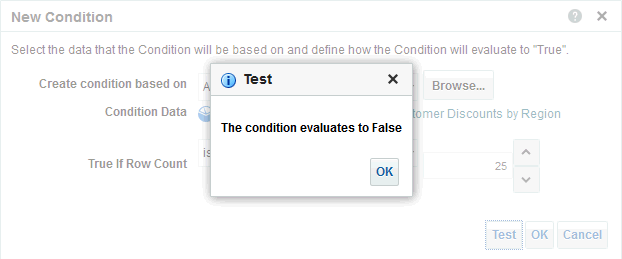
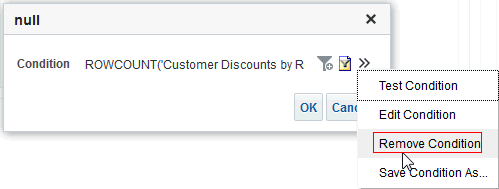
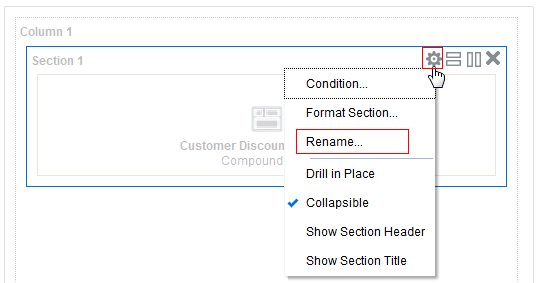









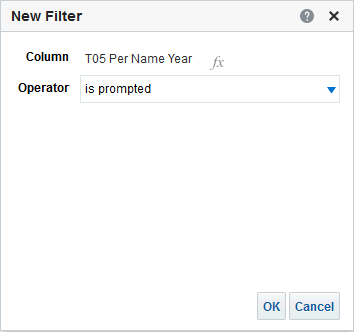


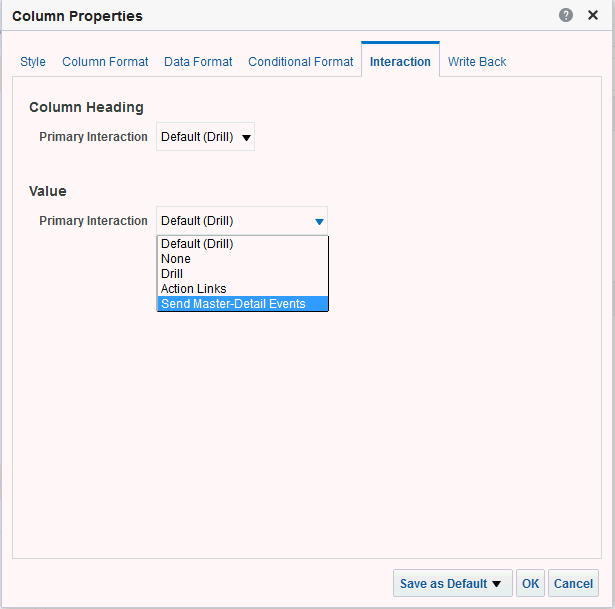
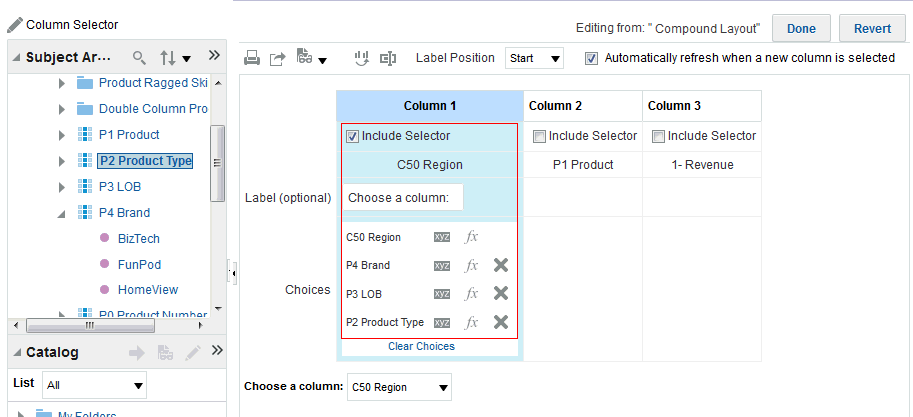
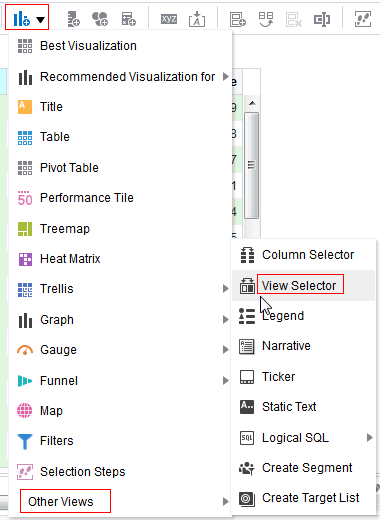
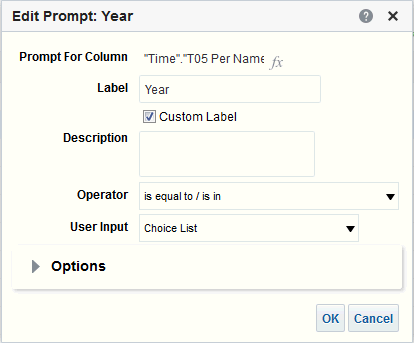
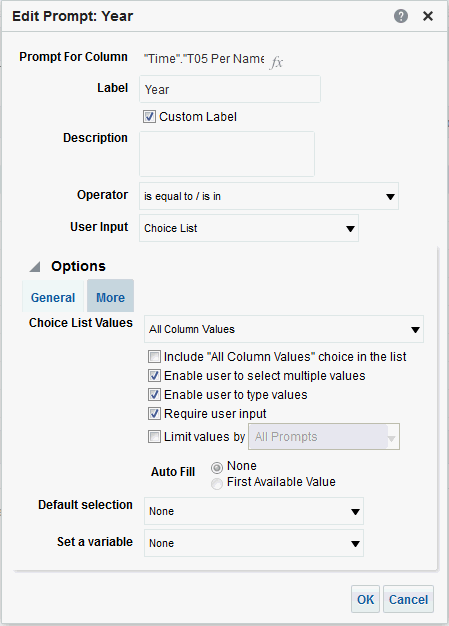
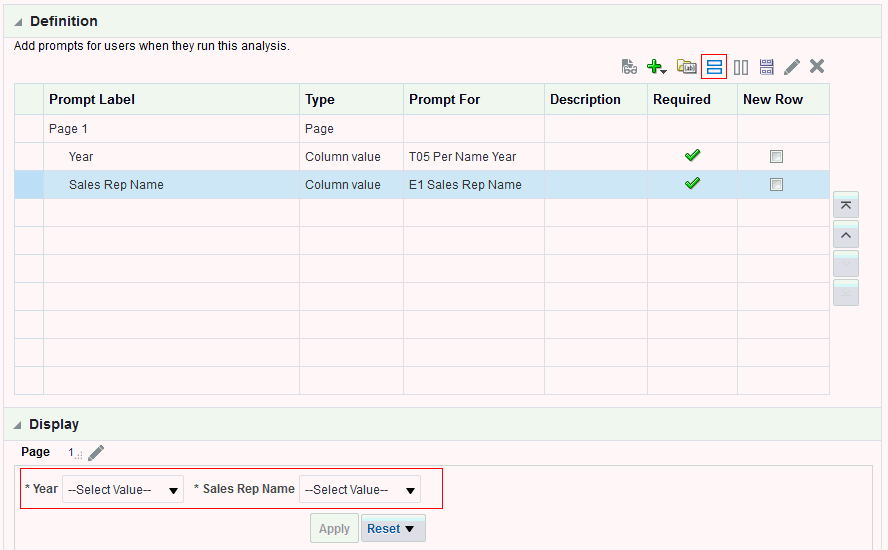
 ), and select Column Prompt.
), and select Column Prompt.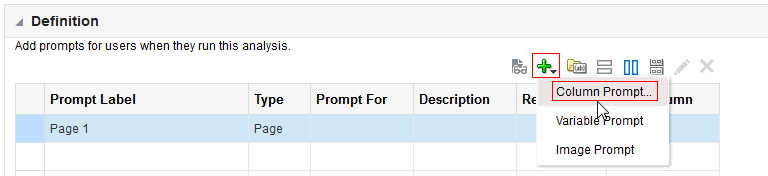
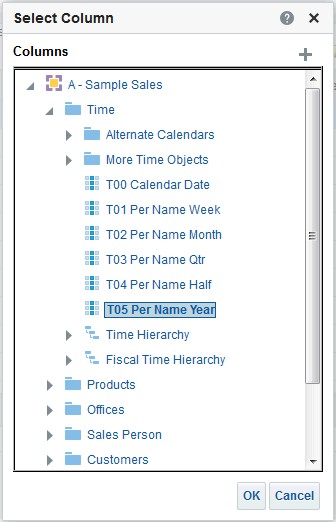
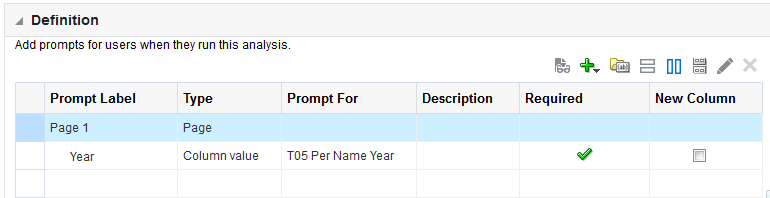
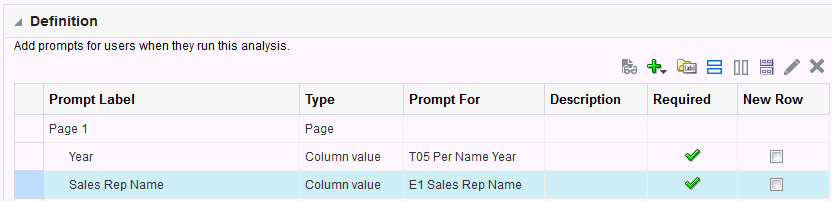

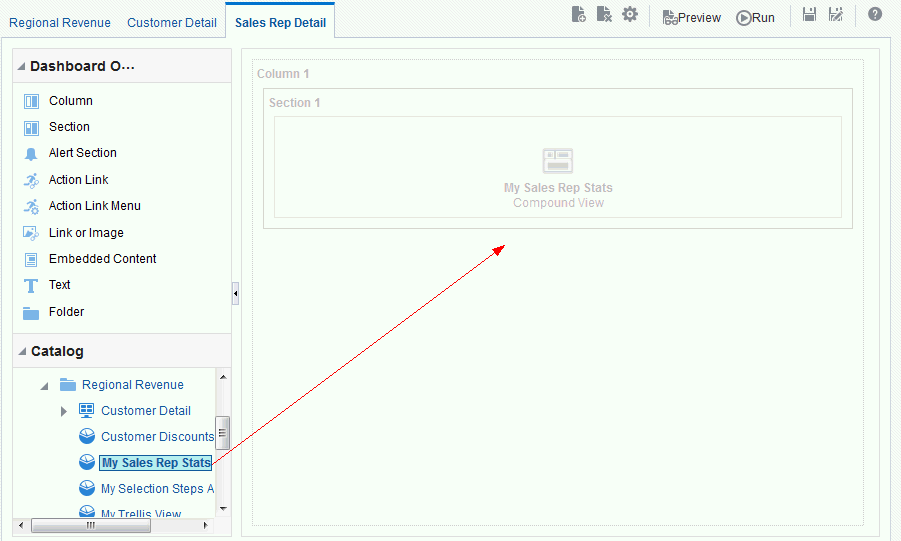
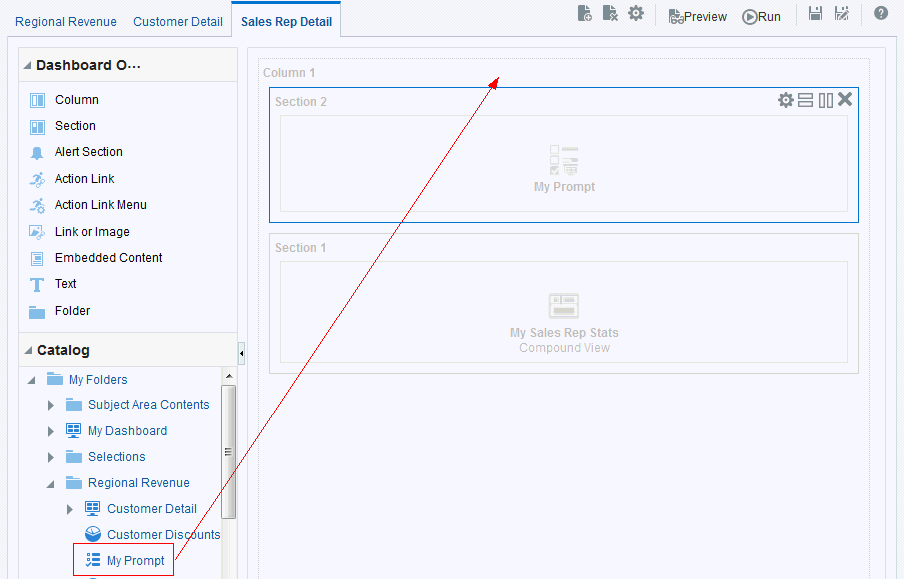
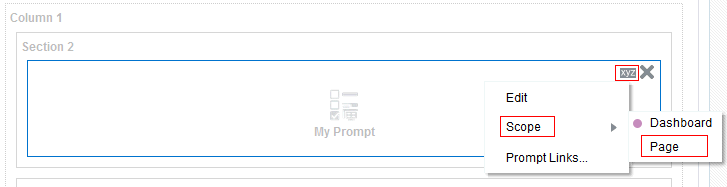
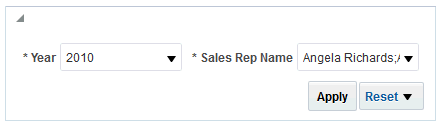
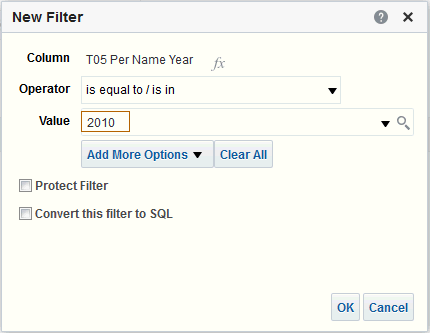
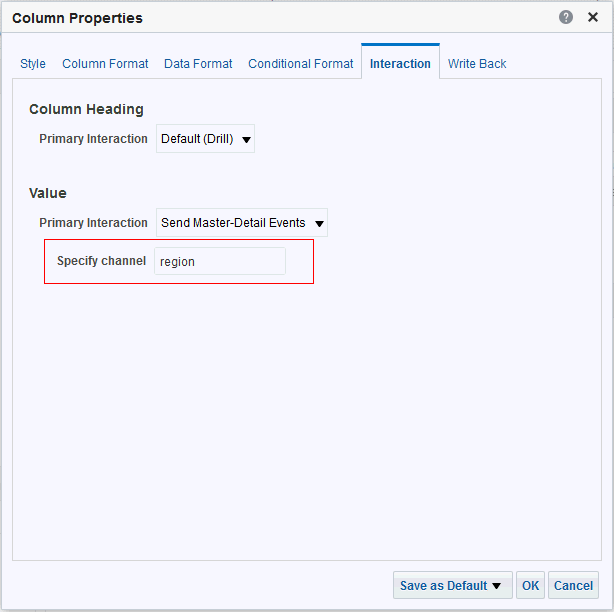
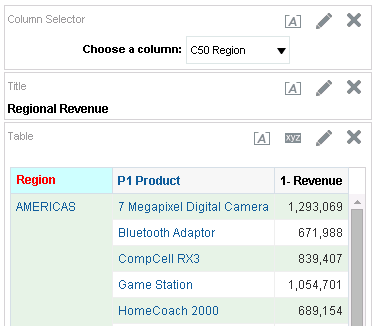
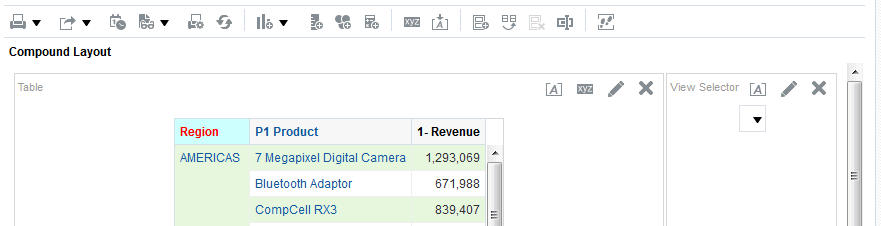
 ) icon, enter a value, and click OK.
) icon, enter a value, and click OK.