Web
services are open standard ( XML, SOAP, HTTP etc.) based Web applications that
interact with other web applications for the purpose of exchanging data.Web
Services can convert your existing applications into Web-applications.
Web services are XML-based information exchange systems that use
the Internet for direct application-to-application interaction. These systems
can include programs, objects, messages, or documents.
The Web Services
Description Language (WSDL, pronounced 'wiz-dəl' or spelled out, 'W-S-D-L') is
an XML-based language that provides a model for describing the functions
of Web
services.
Need
to make SOAP calls to OBIEE WSDL endpoint:
Obiee provides several
webservices that can be reach with their own Url.
The URL has this form:
SOAP
SOAP was originally part of the specification that included the Web Services Description Language (WSDL) and Universal Description, Discovery, and Integration (UDDI). It is used now without WSDL and UDDI. Instead of the discovery process described in the History of the Web Services Specification section below, SOAP messages are hard-coded or genereated without the use of a repository. The interaction is illustrated in the figure below. More on SOAP.
Web Services Description Language
The Web Services Description
Language (WSDL) forms the basis for the original Web Services specification.
The following figure illustrates the use of WSDL. At the left is a service
provider. At the right is a service consumer. The steps involved in providing
and consuming a service are:
1.
A service provider
describes its service using WSDL. This definition is published to a repository
of services. The repository could use Universal Description, Discovery, and
Integration (UDDI). Other forms of directories could also be used.
2.
A service consumer
issues one or more queries to the repository to locate a service and determine
how to communicate with that service.
3.
Part of the WSDL
provided by the service provider is passed to the service consumer. This tells
the service consumer what the requests and responses are for the service
provider.
4.
The service consumer
uses the WSDL to send a request to the service provider.
5.
The service provider
provides the expected response to the service consumer.
Security Service: - This service helps in identifying the user privileges.
One can assign,
revoke privileges using Security Services.
Ibot Service: - As the name suggests, this is a service
for invoking Ibots.
Web Catalog Service:- This
service is for managing the web catalog.
Replication Service:-
This service is used for replication. Export/Import of catalogs can be
done using this.
Metadata Service: - This is for managing the BI Server
metadata.
Report Editing Service: - This
service is used to merge arguments and Oracle BI Web Services
data to create and return the results.
HTMLView Service:- This service is used to embed Oracle BI
HTML results in third-party dynamic
Web pages, such as Active Server Pages (ASP) or JavaServer Pages (JSP), and
portal frameworks. The embed process merges Oracle BI Web Services content with
the content of third-party Web pages.
XMLView Service: This
is used for retrieving the data from Oracle BI EE Server in the form of
XML.
SAWSession Service: This is the service that would enable users
to login, logout and maintain sessions. Now lets see how we can go about
using these services from within Jdeveloper to create a sample custom
report.
USE of SoapUI :-
We can use web services of OBIEE to
accomplish any task that we do in OBIEE like folder creation, report creation,
setting permissions etc.
I used the web services to generate a
session, executeSqlQuery, executeXmlQuery and so on. Below are the steps for
the same:
Step1:-
To
access and understand the structure of webservices I used a tool called SoapUI.
It can be downloaded from the following link: http://www.soapui.org/.
Download the tool and install it.
Step 2:-
Open the SoapUI and
create a project in it using OBIEE’s webservices URL
http://URL:port/analytics/saw.dll/wsdl/v7
Following are the URLs that you would have to use for
each service:-
XMLViewService –
WebCatalogService –
JobManagementService -
Generate a session ID :-
1) In
SoapUI, navigate to SAWSessionService>getSessionVariable>Request1
under the newly created Project.
2) Right click to
open the request editor to alter the xml.
<?xml
version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<soapenv:Envelope
xmlns:soapenv="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/"
xmlns:v7="urn://oracle.bi.webservices/v7">
<soapenv:Header/>
<soapenv:Body>
<v7:logon>
<v7:name>test</v7:name>
<v7:password>*******</v7:password>
</v7:logon>
</soapenv:Body>
</soapenv:Envelope>
4)
Submit the request after adding the parameters (user, pwd) as shown in above
script. This will generate the resulting xml with a session_ID as shown
below:
<soap:Envelope
xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:soapenc="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/encoding/"
xmlns:sawsoap="urn://oracle.bi.webservices/v7">
<soap:Body>
<sawsoap:logonResult>
<sawsoap:sessionID
xsi:type="xsd:string">pfec2ujndlfvchtthr2shpfoisi2kei85tbi2ei</sawsoap:sessionID>
</sawsoap:logonResult>
</soap:Body>
</soap:Envelope>
Use of XMLQuery:- (Read a obiee report) create a new folder test at the following path /sharad/Users/test
1) In SoapUI, navigate to XMLViewServices >executeXMLQuery>Request1
2) Right click to open the request editor to alter the xml.
3) Add the reportPath and sessionID in the xml as shown below
Use
of IbotServices:- create a new ibot at the following any path of OBIEE
In my case created a IBot TEST12 /users/weblogic/test12
1) In
SoapUI, navigate to IBotServices>executeIBotNow>Request1
2) Right click to
open the request editor to alter the xml.
3) Add the reportPath and sessionID in the xml as shown below.
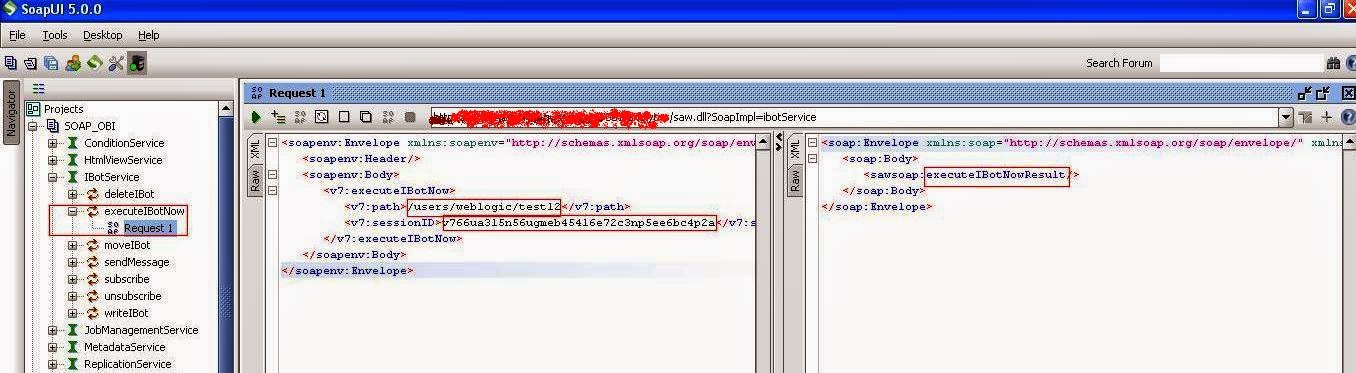
3) Add the reportPath and sessionID in the xml as shown below.


Now Check IBot Destination mail.
Actionable Intelligence
Now Click On
New->Actionable Intelligence ->Action

































